【注意】最后更新于 October 20, 2018,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
ApplicationContext源码解析
一、ApplicationContext体系图
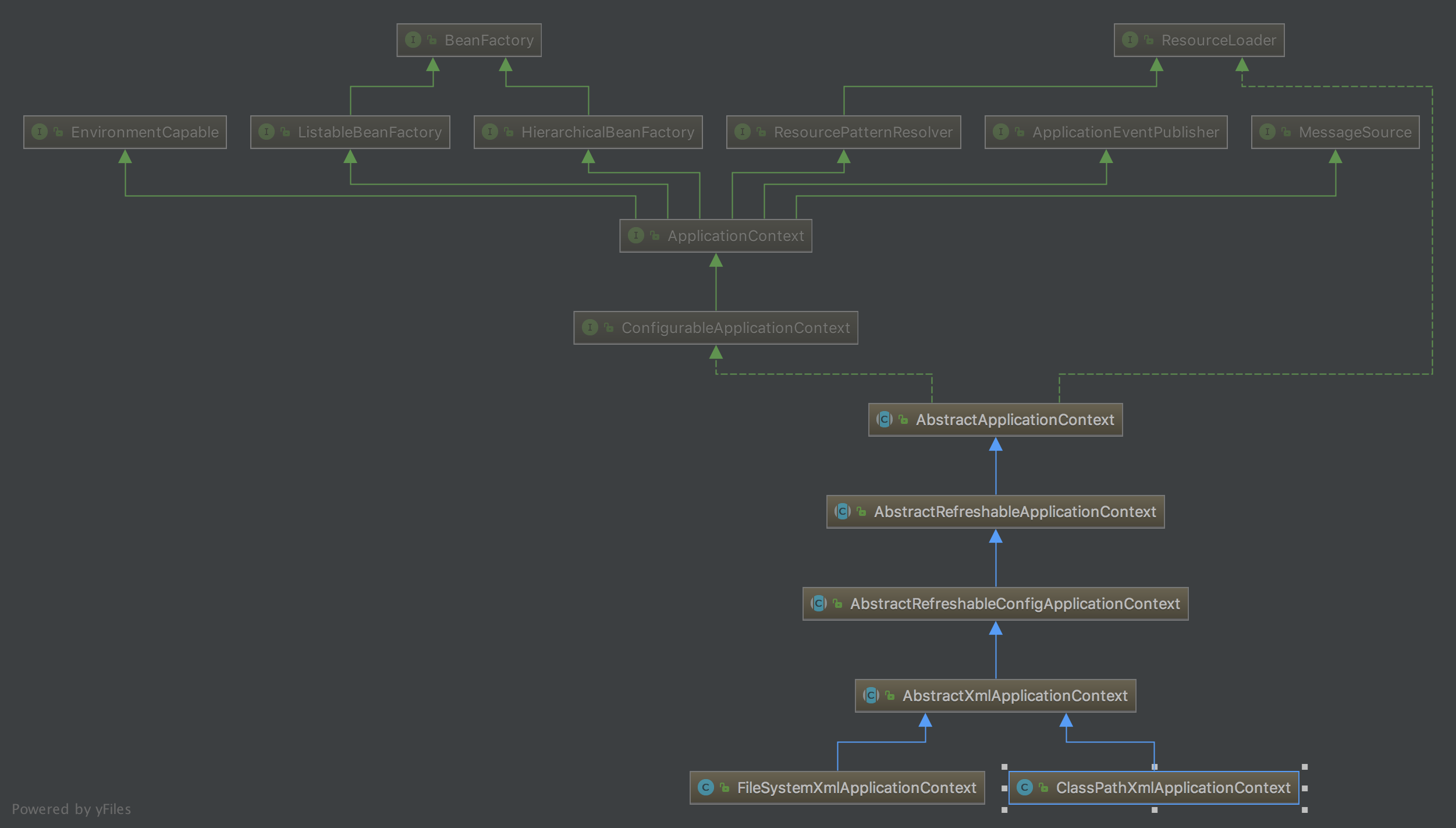
ApplicationContext接口,它由BeanFactory接口派生而来,因而提供BeanFactory所有的功能。ApplicationContext以一种更向面向框架的方式工作以及对上下文进行分层和实现继承,ApplicationContext包还提供了以下的功能:
- MessageSource, 提供国际化的消息访问
- 资源访问,如URL和文件
- 事件传播
二、ApplicationContext refresh操作
1
|
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext applicationContext=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:aspect.xml");
|
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
//配置bean配置地址
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
|
AbstractApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//准备此上下文以进行刷新,设置其启动日期和活动标志以及执行属性源的任何初始化。
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 创建BeanFactory,处理XML 解析一下bean操作
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 准备工作,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean
// 先处理ApplicationContext中BeanFactoryPostProcessors集合BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
// 在处理beanFactory中BeanFactoryPostProcessors集合BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
// 在处理所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//在beanFactory获取BeanPostProcessor对象,注册到beanFactory;
//BeanPostProcessor 优先级排序处理
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//初始化信息源,和国际化相关.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化容器事件传播器.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//为事件传播器注册事件监听器.
// 添加applicationListeners
// 从beanFactory查询ApplicationListener
// 广播earlyApplicationEvents集合
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化所有剩余的单态Bean.
//设置BeanFactory的ConversionService
//对配置了lazy-init属性的单态模式Bean进行预实例化处理
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
//初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
|
1、国际化

- DelegatingMessageSource: 消息源解析委派类(用户未指定时,SpringContext默认使用当前类),功能比较简单:将字符串和参数数组格式化为一个消息字符串
- ResourceBundleMessageSource 依托JDK自带ResourceBundle加载资源,支持绝对路径和工程路径,支持文件为.class文件和.properties。
- ReloadResourceBundleMessageSource依托spring的ResourceLoader加载Resource资源,功能更加强大,同时支持.properties和.xml文件。缓存时间;
如例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>messages</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
|
(1)、getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale)获取国际化对应值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public final String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException {
//1.到messageSource内查找
String msg = getMessageInternal(code, args, locale);
if (msg != null) {
return msg;
}
//2.查找默认的Message
// useCodeAsDefaultMessage为true 返回code,
String fallback = getDefaultMessage(code);
if (fallback != null) {
return fallback;
}
throw new NoSuchMessageException(code, locale);
}
|
(2)、messageSource内查找
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
protected String getMessageInternal(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) {
if (code == null) {
return null;
}
if (locale == null) {
locale = Locale.getDefault();
}
Object[] argsToUse = args;
if (!isAlwaysUseMessageFormat() && ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
// Optimized resolution: no arguments to apply,
// therefore no MessageFormat needs to be involved.
// 优化的解决方案:没有要应用的参数,因此不需要涉及MessageFormat。
// Note that the default implementation still uses MessageFormat;
// this can be overridden in specific subclasses.
// 请注意,默认实现仍使用MessageFormat; 这可以在特定的子类中重写。
String message = resolveCodeWithoutArguments(code, locale);
if (message != null) {
return message;
}
}
else {
// Resolve arguments eagerly, for the case where the message
// is defined in a parent MessageSource but resolvable arguments
// are defined in the child MessageSource.
//处理参数
// 参数类型是MessageSourceResolvable,触发getMessage获取消息
argsToUse = resolveArguments(args, locale);
MessageFormat messageFormat = resolveCode(code, locale);
if (messageFormat != null) {
synchronized (messageFormat) {
return messageFormat.format(argsToUse);
}
}
}
// Check locale-independent common messages for the given message code.
//从公共properties查询
Properties commonMessages = getCommonMessages();
if (commonMessages != null) {
String commonMessage = commonMessages.getProperty(code);
if (commonMessage != null) {
//MessageSourceSupport中把FormatMessage缓存起来;
return formatMessage(commonMessage, args, locale);
}
}
// Not found -> check parent, if any.
//往父类查找
return getMessageFromParent(code, argsToUse, locale);
}
|
(3)、 文件解析
配置文件解析过程为:
注:此处我们可以在AbstractResourceBasedMessageSource中找到此bean的注入参数主要有以下几个:
basenameSet(文件列表set)、defaultEncoding(文件默认编码)、fallbackToSystemLocale(是否使用系统默认的编码)、cacheMillis(cache时间),
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
protected MessageFormat resolveCode(String code, Locale locale) {
Set<String> basenames = getBasenameSet();
for (String basename : basenames) {
//判断是否设定了缓存时间,默认-1为永久保存ResourceBundle,如果大于0,直接重新获取;
ResourceBundle bundle = getResourceBundle(basename, locale);
if (bundle != null) {
//获取MessageFormat
//先从map缓存中获取,无在中ResourceBundle获取,在保存缓存中;
MessageFormat messageFormat = getMessageFormat(bundle, code, locale);
if (messageFormat != null) {
return messageFormat;
}
}
}
return null;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
protected MessageFormat getMessageFormat(ResourceBundle bundle, String code, Locale locale)
throws MissingResourceException {
synchronized (this.cachedBundleMessageFormats) {
Map<String, Map<Locale, MessageFormat>> codeMap = this.cachedBundleMessageFormats.get(bundle);
Map<Locale, MessageFormat> localeMap = null;
if (codeMap != null) {
localeMap = codeMap.get(code);
if (localeMap != null) {
MessageFormat result = localeMap.get(locale);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
String msg = getStringOrNull(bundle, code);
if (msg != null) {
if (codeMap == null) {
codeMap = new HashMap<String, Map<Locale, MessageFormat>>();
this.cachedBundleMessageFormats.put(bundle, codeMap);
}
if (localeMap == null) {
localeMap = new HashMap<Locale, MessageFormat>();
codeMap.put(code, localeMap);
}
MessageFormat result = createMessageFormat(msg, locale);
localeMap.put(locale, result);
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
|
2、事件广播(ApplicationEventMulticaster)
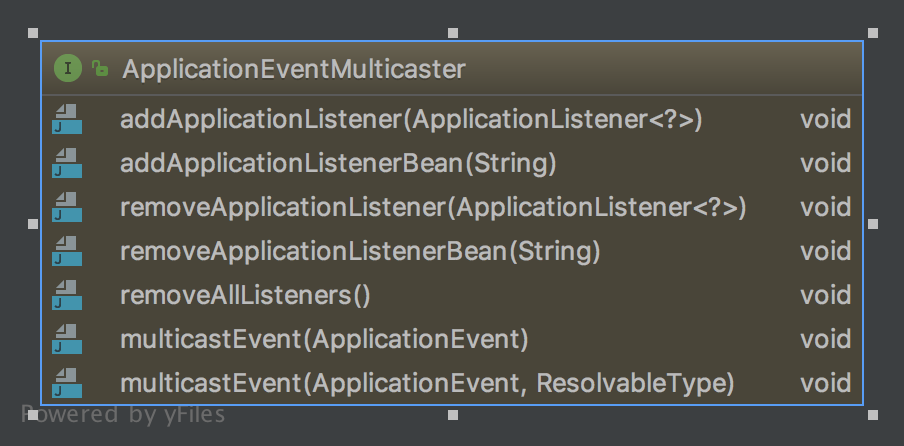
ApplicationEventMulticaster实现类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster;观察者模式一样;
1.添加addApplicationListener
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false);
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// Explicitly remove target for a proxy, if registered already,
// in order to avoid double invocations of the same listener.
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
@Override
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
|
事件保存在ListenerRetriever对象中,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
private class ListenerRetriever {
//保存ApplicationListener集合
public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners;
//保存ApplicationListener的beanName集合
public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans;
//验证是否相同ApplicationListener
private final boolean preFiltered;
public ListenerRetriever(boolean preFiltered) {
this.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>();
this.applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
this.preFiltered = preFiltered;
}
//获取所有ApplicationListener集合
public Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.applicationListeners) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : this.applicationListenerBeans) {
try {
ApplicationListener<?> listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (this.preFiltered || !allListeners.contains(listener)) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
}
|
2.multicastEvent广播事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();//线程池
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {
//触发ApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent方法
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
}
|
3.getApplicationListeners 按类型获取所有ApplicationListener
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
//类加载器是否相同,相同缓存起来
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
//缓存ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
//查询相同类型ApplicationListener集合;
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
//不用缓存ListenerRetriever
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
|
4.ApplicationContext publishEvent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
//不是ApplicationEvent事件 封装成PayloadApplicationEvent
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent)applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
|



