【注意】最后更新于 October 5, 2018,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
Spring的AOP源码分析
一、AOP体系图
1、AOP术语
-
1)连接点(Joinpoint)
程序执行的某个特定位置:如类开始初始化前、类初始化后、类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法抛出异常后。一个类或一段程序代码拥有一些具有边界性质的特定点,
这些点中的特定点就称为“连接点”。Spring仅支持方法的连接点,即仅能在方法调用前、方法调用后、方法抛出异常时以及方法调用前后这些程序执行点织入增强。
连接点由两个信息确定:第一是用方法表示的程序执行点;第二是用相对点表示的方位。
-
2)切点(Pointcut)
每个程序类都拥有多个连接点,如一个拥有两个方法的类,这两个方法都是连接点,即连接点是程序类中客观存在的事物。AOP通过“切点”定位特定的连接点。连接点
相当于数据库中的记录,而切点相当于查询条件。切点和连接点不是一对一的关系,一个切点可以匹配多个连接点。
在Spring中,切点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件,Spring AOP的规则解析引擎负责切点
所设定的查询条件,找到对应的连接点。其实确切地说,不能称之为查询连接点,因为连接点是方法执行前、执行后等包括方位信息的具体程序执行点,而切点只定
位到某个方法上,所以如果希望定位到具体连接点上,还需要提供方位信息。
-
3)通知(Advice)
通知是织入到目标类连接点上的一段程序代码,在Spring中,通知除用于描述一段程序代码外,还拥有另一个和连接点相关的信息,这便是执行点的方位。结合执行点
方位信息和切点信息,我们就可以找到特定的连接点。
-
4)目标对象(Target)
增强逻辑的织入目标类。如果没有AOP,目标业务类需要自己实现所有逻辑,而在AOP的帮助下,目标业务类只实现那些非横切逻辑的程序逻辑,而性能监视和事务管
等这些横切逻辑则可以使用AOP动态织入到特定的连接点上。
-
5)引介(Introduction)
引介是一种特殊的增强,它为类添加一些属性和方法。这样,即使一个业务类原本没有实现某个接口,通过AOP的引介功能,我们可以动态地为该业务类添加接口的实现
逻辑,让业务类成为这个接口的实现类。
-
6)织入(Weaving)
织入是将增强添加对目标类具体连接点上的过程。AOP像一台织布机,将目标类、增强或引介通过AOP这台织布机天衣无缝地编织到一起。根据不同的实现技术,AOP有三
种织入的方式:
a、编译期织入,这要求使用特殊的Java编译器。
b、类装载期织入,这要求使用特殊的类装载器。
c、动态代理织入,在运行期为目标类添加增强生成子类的方式。
Spring采用动态代理织入,而AspectJ采用编译期织入和类装载期织入。
-
7)代理(Proxy)
一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产出了一个结果类,它是融合了原类和增强逻辑的代理类。根据不同的代理方式,代理类既可能是和原类具有相同接口的类,也可能就是原类
的子类,所以我们可以采用调用原类相同的方式调用代理类。
-
8)切面(Aspect)
切面由切点和增强(引介)组成,它既包括了横切逻辑的定义,也包括了连接点的定义,Spring AOP就是负责实施切面的框架,它将切面所定义的横切逻辑织入到切面
所指定的连接点中。
2、Advice接口
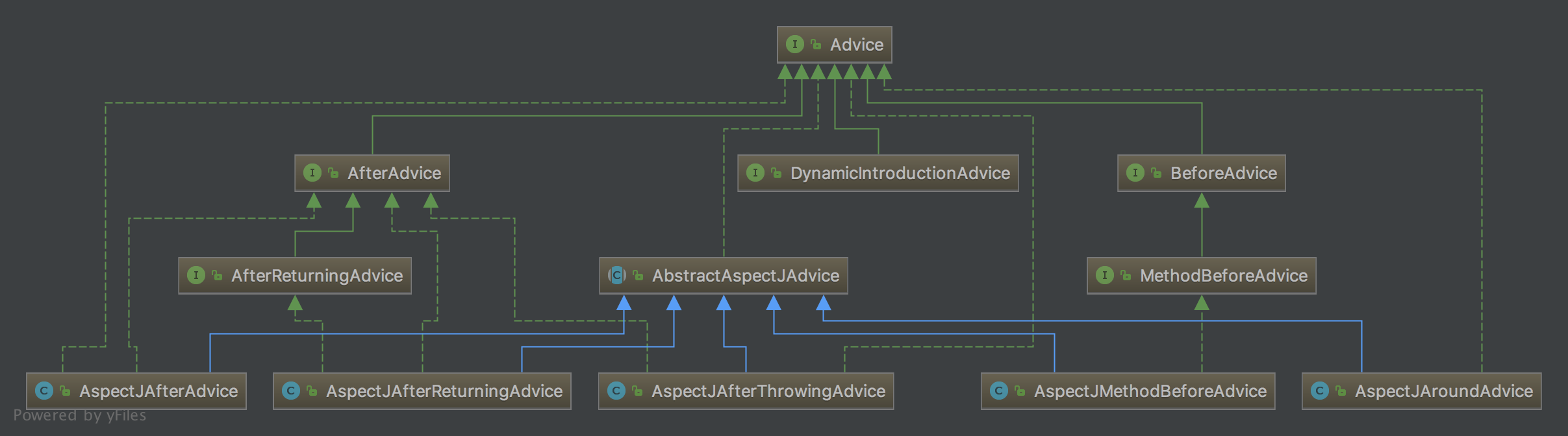
3、MethodInterceptor接口
将所有的advice都要最终转化成MethodInterceptor,它的invoke接口方法包含了拦截器要执行的内容及执行的顺序。
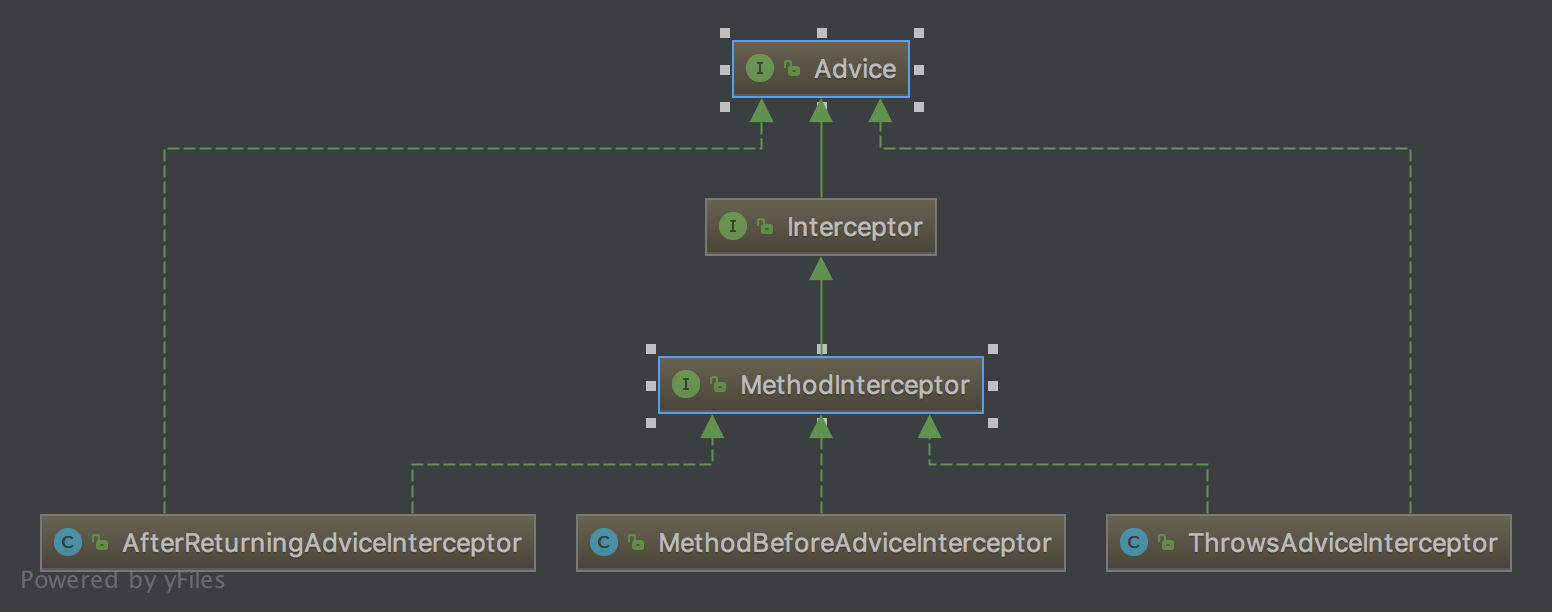
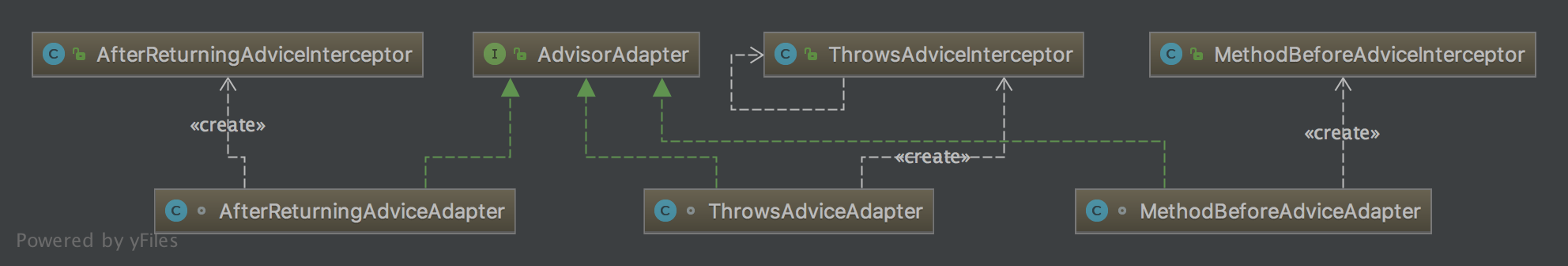
4、AdvisorAdapter接口
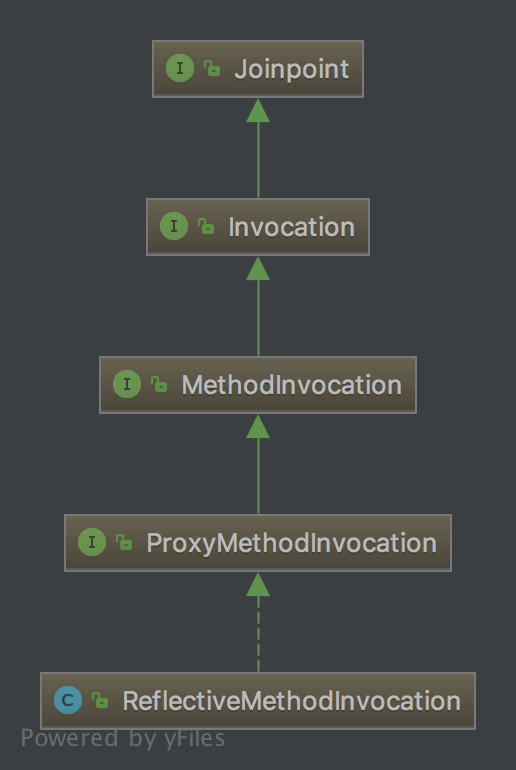
5、Joinpoint接口
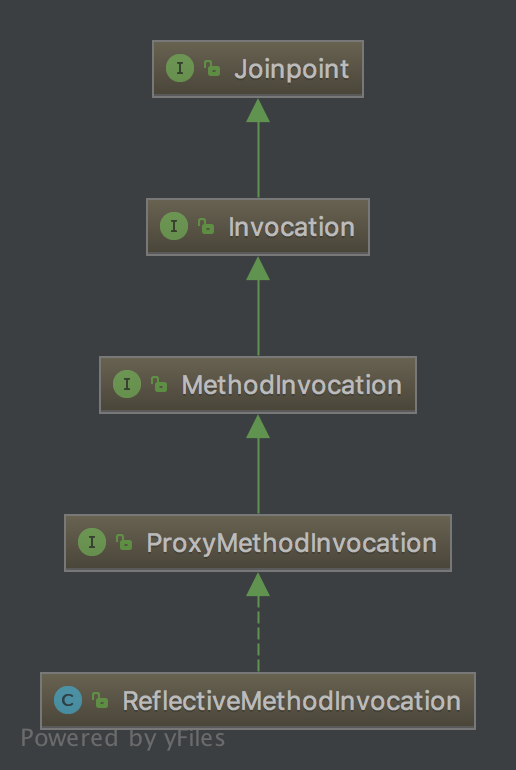
6、Advisor接口
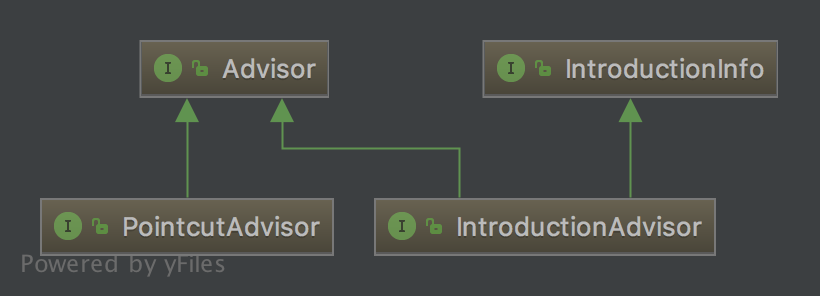
7、Joinpoint接口
二、xml解析AOP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="TestAspect" ref="test01Aspect">
<!– 配置com.spring.service包下所有类或接口的所有方法 –>
<aop:pointcut id="businessService"
expression="execution(* com.zp.aspect.*.*(..))" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doBefore"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doAfter"/>
<aop:around pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doAround"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="businessService" method="doThrowing" throwing="ex"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
|
自定义aop标签,AopNamespaceHandler处理;
1
2
3
|
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
|
1、AspectJPointcutAdvisor和AspectJExpressionPointcut
“aop:before”,“aop:after"等注册AspectJPointcutAdvisor;构造参数AbstractAspectJAdvice,找到对应实现类;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private Class<?> getAdviceClass(Element adviceElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
String elementName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(adviceElement);
if (BEFORE.equals(elementName)) {
return AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice.class;
}
else if (AFTER.equals(elementName)) {
return AspectJAfterAdvice.class;
}
else if (AFTER_RETURNING_ELEMENT.equals(elementName)) {
return AspectJAfterReturningAdvice.class;
}
else if (AFTER_THROWING_ELEMENT.equals(elementName)) {
return AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.class;
}
else if (AROUND.equals(elementName)) {
return AspectJAroundAdvice.class;
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown advice kind [" + elementName + "].");
}
}
|
“aop:pointcut"注册AspectJExpressionPointcut;
2、AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator注册到容器中;两个proxyTargetClass和exposeProxy属性;
proxyTargetClass是作用是为true,cglib代理,false为JDK代理;现在版本默认true;exposeProxy属性作用为true,在线程内部暴露出代理对象(ThreadLocal实现);
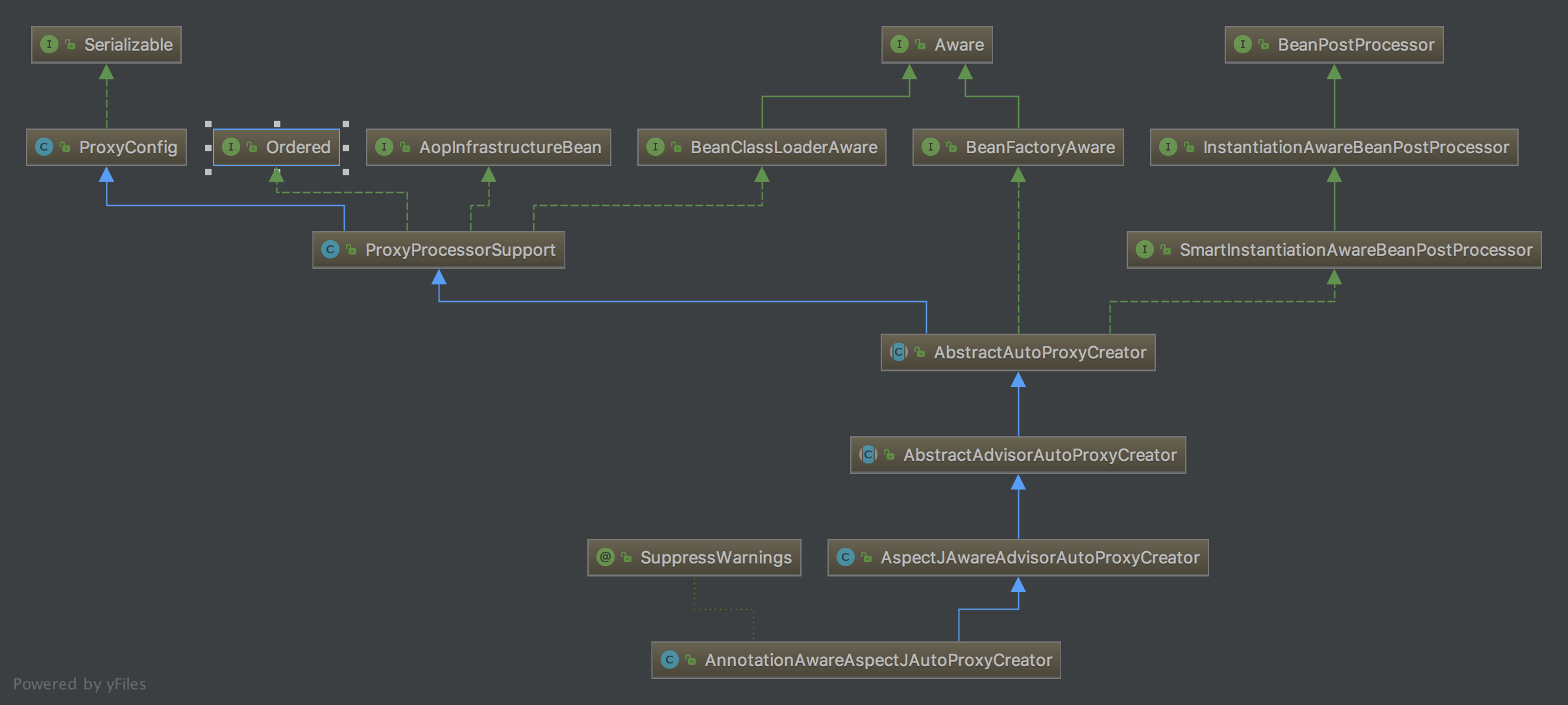
(1).ProxyConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//true,cglib代理,false为JDK代理
private boolean proxyTargetClass = false;
//是否执行某些优化
private boolean optimize = false;
//代表子类是否能被转换为Advised接口,默认为false,表示可以
boolean opaque = false;
//为true,在线程内部暴露出代理对象
boolean exposeProxy = false;
//当前代理配置是否被冻结,如果被冻结,配置将不能被修改
private boolean frozen = false;
|
配置信息
(2).BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization
创建对象是调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization,AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
// 过滤AOP接口;
if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.如果我们有自定义TargetSource,请在此处创建代理。
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean: 禁止目标bean的不必要的默认实例化:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.TargetSource将以自定义方式处理目标实例。
if (beanName != null) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
//获取Advisor集合
// 先获取Advisor接口对象,
// 在获取advisor集合中添加ExposeInvocationInterceptor添加到第一位
// 在进行排序
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
//创建代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
|
(3).createProxy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//1.创建ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//2.设置poxyConfig配置信息
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//2.设置Advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
//3.设置目标对象
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//4.创建代理对象,DefaultAopProxyFactory根据你的配置生产cglib代理对象活着JDK代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
|
(4).cglib代理调用方法处理DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);//把代理对象保存ThreadLocal
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
//把Advisor转化为MethodInterceptor
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
// chain为空直接反射调用目标对象
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
|
CglibMethodInvocation 是MethodInterceptor调用连开始
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
//动态方法匹配器
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
//动态匹配失败。, 跳过此拦截器并调用链中的下一个。
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
/**
* Invoke the joinpoint using reflection.
* Subclasses can override this to use custom invocation.
* @return the return value of the joinpoint
* @throws Throwable if invoking the joinpoint resulted in an exception
*/
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
|
流程处理:
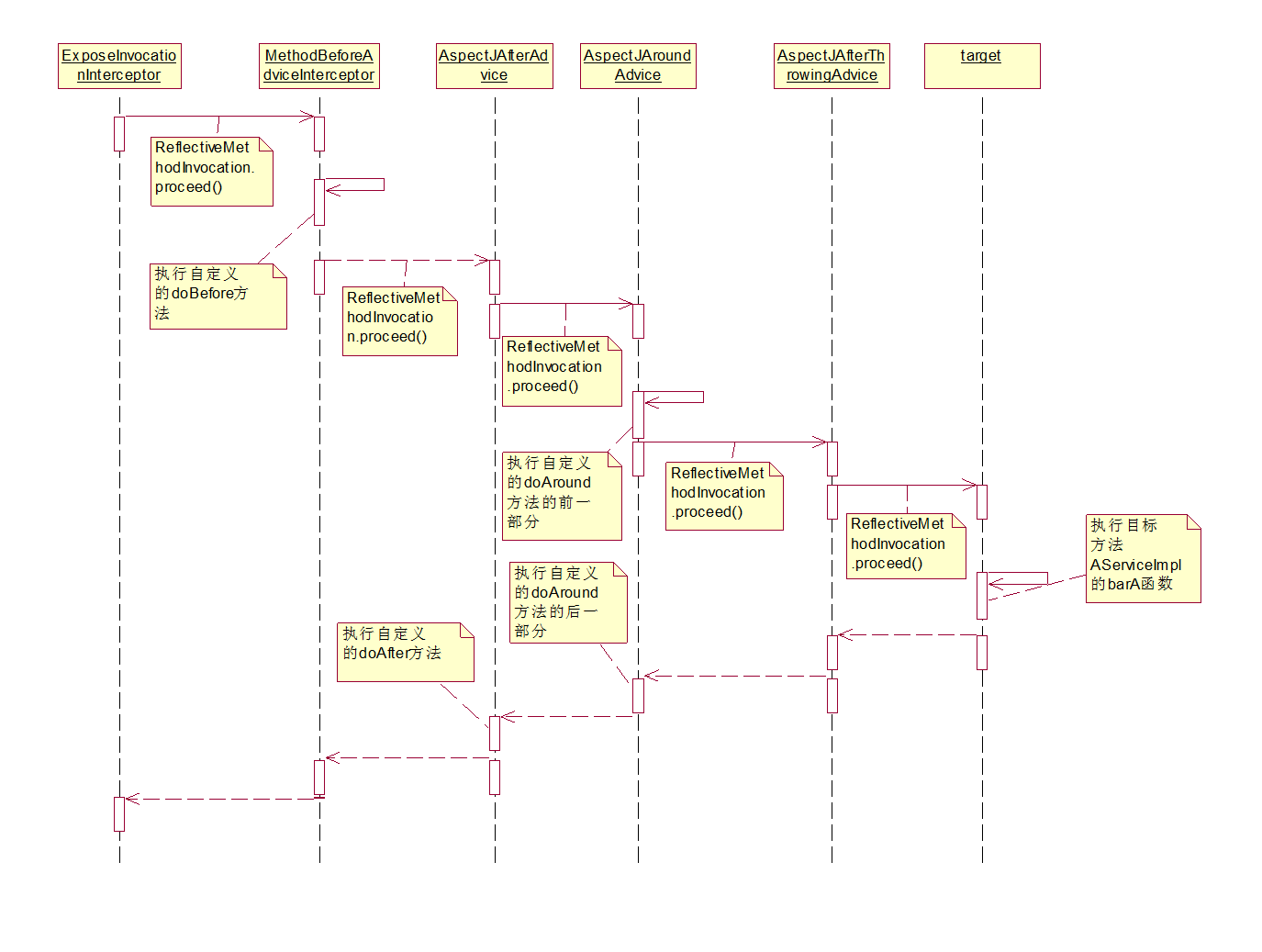
三、注释解析AOP
1
|
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
|
开启注解形式
AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser把AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator注册到容器中;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
//注解查询Advisors,生成InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
}
|
运用aspectj;我个人了解逻辑蛮复杂








