【注意】最后更新于 March 23, 2019,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
一、介绍
Channelpipeline是 Channelhandler的容器,它负责 Channelhandler的管理和事件拦截与调度。
事件如何在流水线中流动如图下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
* I/O Request
* via {@link Channel} or
* {@link ChannelHandlerContext}
* |
* +---------------------------------------------------+---------------+
* | ChannelPipeline | |
* | \|/ |
* | +---------------------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | | Inbound Handler N | | Outbound Handler 1 | |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | /|\ | |
* | | \|/ |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | | Inbound Handler N-1 | | Outbound Handler 2 | |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | /|\ . |
* | . . |
* | ChannelHandlerContext.fireIN_EVT() ChannelHandlerContext.OUT_EVT()|
* | [ method call] [method call] |
* | . . |
* | . \|/ |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | | Inbound Handler 2 | | Outbound Handler M-1 | |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | /|\ | |
* | | \|/ |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | | Inbound Handler 1 | | Outbound Handler M | |
* | +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
* | /|\ | |
* +---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
* | \|/
* +---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
* | | | |
* | [ Socket.read() ] [ Socket.write() ] |
* | |
* | Netty Internal I/O Threads (Transport Implementation) |
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------+
*
|
消息的读取和发送处理全流程描述如下:
-
1)底层的Socket.read()方法读取ByteBuf,触发Channelread事件,由IO线程 Nioeventloop调用 Channelpipeline的fireChannelread(Object msg)方法,将消息
(ByteBuf)传输到 Channelpipeline中,将消息依次被 Inbound Handler 1、 Inbound Handler 2、 Inbound Handler N拦截和处理,在这个过程中,
任何Channelhandler都可以中断当前的流程,结束消息的传递。
-
2)调用ChannelHandlerContext的wrte方法发送消息,将消息依次被Outbound Handler 1,Outbound Handler 2 ,Outbound Handler M 拦截和处理,最终交给Socket.write()发送消息;
将事件转发给下一个处理程序
正如上图所看到的那样,处理程序必须调用ChannelHandlerContext中的事件传播方法才能将事件转发到其下一个处理程序。这些方法包括:
-
Inbound 事件传播方法:
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRegistered() Channel注册事件
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelActive() TCP链路建立成功, Channel激活事件;
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(Object) 读事件
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelReadComplete() 读操作完成通知事件;
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireExceptionCaught(Throwable) 异常通知事件;
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireUserEventTriggered(Object) 用户自定义事件
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelWritabilityChanged() Channel的可写状态变化通知事件;
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelInactive() TCP连接关闭,链路不可用通知事件。
-
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelUnregistered() Channel从EventLoop中注销
-
Outbound 事件传播方法:
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.bind(SocketAddress, ChannelPromise)
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.connect(SocketAddress, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise)
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.write(Object, ChannelPromise)
-
ChannelHandlerContext.flush()
-
ChannelHandlerContext.read()
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.disconnect(ChannelPromise)
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.close(ChannelPromise)
-
ChannelOutboundInvoker.deregister(ChannelPromise)
线程安全:
Channelpipeline是线程安全的,这意味着N个业务线程可以并发地操作Channelpipeline而不存在多线程并发问题。但是, Channelhandler却不是线程安全的,这意味着尽管
Channelpipeline是线程安全的,但是用户仍然需要自己保证Channelhandler的线程安全,ChannelHandler可以随时添加或删除;
uml关系如图下:
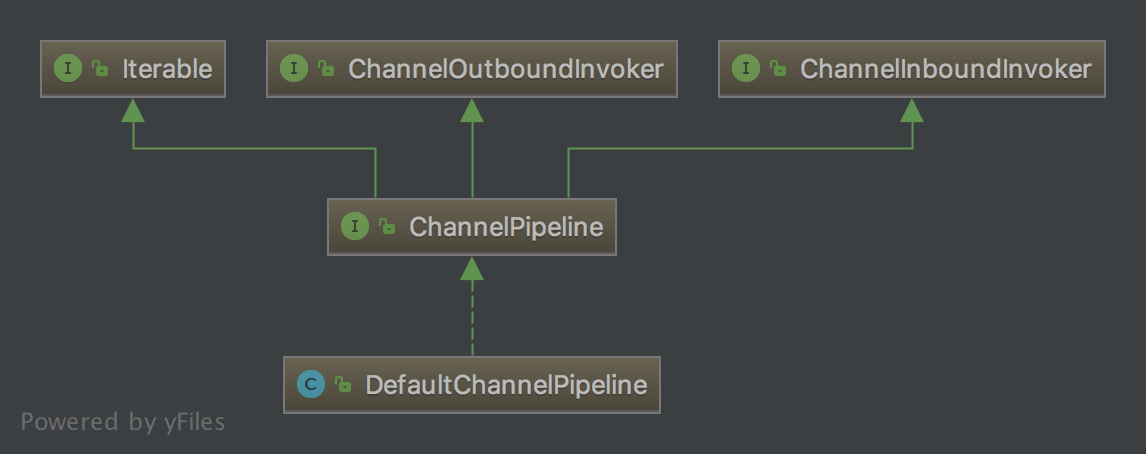
二、 DefaultChannelPipeline源码分析
1.数据结构
- 以双链表保存ChannelHandler的数据
- head和tail变量,控制往下处理或者往上处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
private static final String HEAD_NAME = generateName0(HeadContext.class);
private static final String TAIL_NAME = generateName0(TailContext.class);
private static final FastThreadLocal<Map<Class<?>, String>> nameCaches =
new FastThreadLocal<Map<Class<?>, String>>() {
@Override
protected Map<Class<?>, String> initialValue() throws Exception {
return new WeakHashMap<Class<?>, String>();
}
};
private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<DefaultChannelPipeline, MessageSizeEstimator.Handle> ESTIMATOR =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(
DefaultChannelPipeline.class, MessageSizeEstimator.Handle.class, "estimatorHandle");
//AbstractChannelHandlerContext中有prev,next属性形成双链表;Inbound和Outbound事件都在在这个抽象类实现;
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext head; //头节点,
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext tail; //尾节点
private final Channel channel;
private final ChannelFuture succeededFuture;
private final VoidChannelPromise voidPromise;
private final boolean touch = ResourceLeakDetector.isEnabled();
//线程池中的线程映射,记住这个映射是为了保证执行任务时使用同一个线程
private Map<EventExecutorGroup, EventExecutor> childExecutors;
private volatile MessageSizeEstimator.Handle estimatorHandle; //负责估计消息的大小
private final boolean firstRegistration = true;//对应Channel首次注册到EventLoop
//未注册,添加或者删除ChannelHandler预备存放地方,单链表存储
private PendingHandlerCallback pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
//Channel被注册,就设置为true。一旦设置为true,值将不会改变。
private boolean registered;
}
|
2.构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this);//头节点
head = new HeadContext(this);//尾节点
//头节点和尾节点相互链接
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
|
3.addFirst 添加ChannelHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline addFirst(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) {
// 1.验证未被@Sharable注解时,一个实例是否重复使用
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// 2.名称重复样子,以及name为空,自动生成名字,生成名字规则按类名
name = filterName(name, handler);
// 3.创建AbstractChannelHandlerContext
newCtx = newContext(group, name, handler);
// 4.添加双链表中
addFirst0(newCtx);
// 5.未注册,PendingHandlerCallback任务添加到pendingHandlerCallbackHead链表中;
// 分添加(PendingHandlerCallback)或者删除任务(PendingHandlerRemovedTask)
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending(); //设置AbstractChannelHandlerContext中状态,INIT改成ADD_PENDING
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
// 6.当前线程不是EventLoop线程,是直接callHandlerAdded0;不是添加任务执行callHandlerAdded0
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) { //当前线程不是EventLoop线程
newCtx.setAddPending();
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
}
});
return this;
}
}
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
|
(1).checkMultiplicity 验证@Sharable注解,未被@Sharable注解时,指定ChannelHandler对象ChannelPipeline只能添加一次;被@Sharable注解时,可以添加多次;
- handler继承ChannelHandlerAdapter,才能做下面判断
- 类注解@Sharable,一个实例添加多次添加
- 没有类注解@Sharable,一个实例只能添加一次,以added做验证
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private static void checkMultiplicity(ChannelHandler handler) {
if (handler instanceof ChannelHandlerAdapter) {
ChannelHandlerAdapter h = (ChannelHandlerAdapter) handler;
if (!h.isSharable() && h.added) { //验证ChannelHandler对象未被@Sharable注解时,ChannelPipeline只能添加一次;
throw new ChannelPipelineException(...);
}
h.added = true;
}
}
|
(2).filterName name为空自动生成名称,name不为空,验证名称是否重复
- 参数name为NULL,自动生成名字
- 检查重复名称
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
private String filterName(String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
if (name == null) { //名称为空,自动生成名称,
return generateName(handler);
}
checkDuplicateName(name); //检查重复名称
return name;
}
//按handler类自动生成名字
private String generateName(ChannelHandler handler) {
Map<Class<?>, String> cache = nameCaches.get();
Class<?> handlerType = handler.getClass();
String name = cache.get(handlerType);/先从缓存中获取名称
if (name == null) {
name = generateName0(handlerType); //按类名称自动生成名称
cache.put(handlerType, name); //保存在缓存中
}
//用户不太可能放置多个相同类型的处理程序,但要确保避免任何名称冲突。请注意,我们不会缓存这里生成的名称。
if (context0(name) != null) {
String baseName = name.substring(0, name.length() - 1); // Strip the trailing '0'.
//有相同名称,baseName把后面#0的0累加生成新名称;
for (int i = 1;; i ++) {
String newName = baseName + i;
if (context0(newName) == null) {
name = newName;
break;
}
}
}
return name;
}
//生成名称规则 handlerType=com.zp.HelloChannelHandler 形成名称=HelloChannelHandler#0
private static String generateName0(Class<?> handlerType) {
return StringUtil.simpleClassName(handlerType) + "#0";
}
|
(3).newContext 创建AbstractChannelHandlerContext,这个类在后面具体分析;
- ChannelHandler包装成ChannelHandlerContext;
1
2
3
|
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext newContext(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
return new DefaultChannelHandlerContext(this, childExecutor(group), name, handler);
}
|
a.childExecutor(group)
- 根据ChannelOption.SINGLE_EVENTEXECUTOR_PER_GROUP配置,按线程组是否公用相同的线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private EventExecutor childExecutor(EventExecutorGroup group) {
if (group == null) {
return null;
}
//单独执行任务
Boolean pinEventExecutor = channel.config().getOption(ChannelOption.SINGLE_EVENTEXECUTOR_PER_GROUP);
if (pinEventExecutor != null && !pinEventExecutor) {
return group.next();
}
Map<EventExecutorGroup, EventExecutor> childExecutors = this.childExecutors;
if (childExecutors == null) {
childExecutors = this.childExecutors = new IdentityHashMap<EventExecutorGroup, EventExecutor>(4);
}
EventExecutor childExecutor = childExecutors.get(group);
if (childExecutor == null) {
childExecutor = group.next();
childExecutors.put(group, childExecutor);
}
return childExecutor;
}
|
(4).addFirst0 拼接到head后面
链表添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private void addFirst0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext nextCtx = head.next;
newCtx.prev = head;
newCtx.next = nextCtx;
head.next = newCtx;
nextCtx.prev = newCtx;
}
|
(5).callHandlerCallbackLater registered为false,把回调任务添加到pendingHandlerCallbackHead链表中;
- pendingHandlerCallbackHead添加任务,单链表结构
- 分两种类型PendingHandlerCallbackPendingHandlerCallback和PendingHandlerRemovedTask
- 调用callHandlerAdded0方法以及callHandlerAdded0
- Channel注册调用channelRegistered方法,处理回调任务链表集合;处理方法invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private void callHandlerCallbackLater(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, boolean added) {
assert !registered;
PendingHandlerCallback task = added ? new PendingHandlerCallbackPendingHandlerCallback(ctx) : new PendingHandlerRemovedTask(ctx);
PendingHandlerCallback pending = pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
if (pending == null) {
pendingHandlerCallbackHead = task;
} else {
// Find the tail of the linked-list.
while (pending.next != null) {
pending = pending.next;
}
pending.next = task;
}
}
|
a.PendingHandlerAddedTask 和PendingHandlerRemovedTask源码分析
PendingHandlerCallback抽象类是PendingHandlerAddedTask 和PendingHandlerRemovedTask父类;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
private abstract static class PendingHandlerCallback implements Runnable {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx;
PendingHandlerCallback next; //单链表实现;保存集合
PendingHandlerCallback(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
abstract void execute();
}
|
PendingHandlerAddedTask 等待添加任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
private final class PendingHandlerAddedTask extends PendingHandlerCallback {
PendingHandlerAddedTask(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super(ctx);
}
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(ctx);
}
@Override
void execute() {
EventExecutor executor = ctx.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
callHandlerAdded0(ctx);
} else {
try {
executor.execute(this);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
...
remove0(ctx);
ctx.setRemoved();
}
}
}
}
|
PendingHandlerRemovedTask 等待删除任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
private final class PendingHandlerRemovedTask extends PendingHandlerCallback {
PendingHandlerRemovedTask(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super(ctx);
}
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
}
@Override
void execute() {
EventExecutor executor = ctx.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
} else {
try {
executor.execute(this);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
...
ctx.setRemoved();
}
}
}
}
|
b.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded 处理理回调任务链表pendingHandlerCallbackHead集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
final void invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded() {
assert channel.eventLoop().inEventLoop();
if (firstRegistration) {
firstRegistration = false;
//我们现在注册到EventLoop。现在是时候调用ChannelHandlers的回调了,这是在注册完成之前添加的。
callHandlerAddedForAllHandlers();
}
}
private void callHandlerAddedForAllHandlers() {
final PendingHandlerCallback pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
synchronized (this) {
assert !registered;
// This Channel itself was registered.
registered = true;
pendingHandlerCallbackHead = this.pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
// Null out so it can be GC'ed.
this.pendingHandlerCallbackHead = null;
}
PendingHandlerCallback task = pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
while (task != null) {
task.execute(); //执行任务
task = task.next;
}
}
|
(6).callHandlerAdded0 通知添加完成处理两个方法ChannelHandler.handlerAdded和AbstractChannelHandlerContext.setAddComplete
- 通知ChannelHandler.handlerAdded方法
- 通知AbstractChannelHandlerContext.setAddComplete方法,ADD_COMPLETE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
private void callHandlerAdded0(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
ctx.handler().handlerAdded(ctx); //通知ChannelHandler.handlerAdded方法
ctx.setAddComplete(); //通知AbstractChannelHandlerContext.setAddComplete方法,ADD_COMPLETE
} catch (Throwable t) { //通知异常处理
boolean removed = false;
try {
remove0(ctx);
try {
ctx.handler().handlerRemoved(ctx);//通知ChannelHandler.handlerRemoved方法
} finally {
ctx.setRemoved(); //通知ChannelHandler.setRemoved方法 REMOVE_COMPLETE
}
removed = true;
} catch (Throwable t2) {
...
}
if (removed) {
fireExceptionCaught(new ChannelPipelineException(...));//异常通知事件
} else {
fireExceptionCaught(new ChannelPipelineException(...));//异常通知事件
}
}
}
|
a.remove0 移除AbstractChannelHandlerContext链表中
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
private static void remove0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = ctx.prev;
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = ctx.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
|
(7).callHandlerRemoved0 删除完成通知
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
private void callHandlerRemoved0(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
// Notify the complete removal.
try {
try {
ctx.handler().handlerRemoved(ctx);//通知ChannelHandler.handlerRemoved方法
} finally {
ctx.setRemoved(); //通知ChannelHandler.setRemoved方法
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
fireExceptionCaught(new ChannelPipelineException(...));
}
}
|
4.addLast,addBefore都类同,双链表操作
5.remove 删除指定AbstractChannelHandlerContext
6.replace 替换指定AbstractChannelHandlerContext
6.destroy pipeline中的所有节点销毁,顺序由尾部向头部并触发handlerRemoved()
7.Inbound 事件方法
- head触发,判断事件执行器是否当前线程,是立即执行head的事件,不是,提交任务执行;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRegistered() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRegistered(head);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelUnregistered() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelUnregistered(head);
return this;
}
|
8.Outbound 事件方法
tail执行,tail是Inbound事件;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Override
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return tail.bind(localAddress);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
return tail.connect(remoteAddress);
}
|
tail就是TailContext对象,TailContext实现AbstractChannelHandlerContext抽象类;具有AbstractChannelHandlerContext特性;
三、 AbstractChannelHandlerContext源码分析
AbstractChannelHandlerContext抽象类继承ChannelHandlerContext,具有ChannelHandlerContext.Inbound和ChannelHandlerContext.Outbound事件特性;
AbstractChannelHandlerContext的UML图
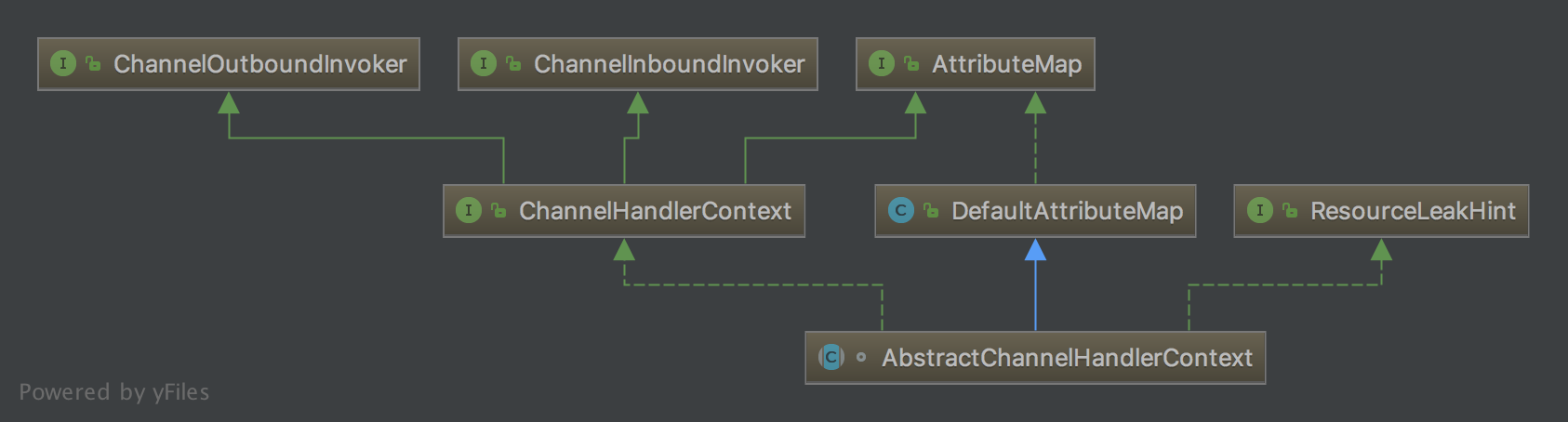
1.数据结构
- 双链表结构
- handlerState 状态控制是否执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext extends DefaultAttributeMap
implements ChannelHandlerContext, ResourceLeakHint {
//双向链表
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next;//下节点
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev;//前节点
//CAS 修改handlerState属性
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractChannelHandlerContext> HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.class, "handlerState");
//handlerState 几个状态标示
//等待添加状态
private static final int ADD_PENDING = 1;
//添加状态
private static final int ADD_COMPLETE = 2;
//删除状态
private static final int REMOVE_COMPLETE = 3;
//初始化状态
private static final int INIT = 0;
private final boolean inbound;//inbound事件状态
private final boolean outbound;//outbound事件状态
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
private final String name; //ChannelHandler名称
//如果由EventLoop或给定的EventExecutor的是OrderedEventExecutor的实例,则它是有序的。
private final boolean ordered;
//如果不使用子执行程序,将被设置为null,否则将被设置为子执行程序。
final EventExecutor executor;
private ChannelFuture succeededFuture;
//状态,初始化 INIT
private final int handlerState = INIT;
}
|
2.构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name,
boolean inbound, boolean outbound) {
this.name = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(name, "name");
this.pipeline = pipeline;
this.executor = executor;
this.inbound = inbound;
this.outbound = outbound;
//如果由EventLoop或给定的EventExecutor的是OrderedEventExecutor的实例,则它是有序的。
ordered = executor == null || executor instanceof OrderedEventExecutor;
}
|
3.executor 获取事件执行器(就是个线程)
没有指定事件执行器就用Channel的事件执行去
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Override
public EventExecutor executor() {
if (executor == null) {
return channel().eventLoop();
} else {
return executor;
}
}
|
4.findContextInbound 查找Inbound事件的ChannelHandlerContext
往下个节点查询,inbound为true的ChannelHandlerContext;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
|
5.Inbound事件
(1).fireChannelRegistered() 触发next的注册事件
分三个步骤执行:
- 查找next的ChannelHandlerContext
- 调用next个ChannelHandlerContext#invokeChannelRegistered方法
- 执行ChannelInboundHandler#channelRegistered
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered() {
invokeChannelRegistered(findContextInbound());
return this;
}
|
a.findContextInbound 查找next的ChannelHandlerContext
往下个节点查询,inbound为true的ChannelHandlerContext;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
|
b.invokeChannelRegistered 调用next个ChannelHandlerContext#invokeChannelRegistered方法
- 获取next的事件执行器,是相同线程就立即执行invokeChannelRegistered,不是提交任务执行;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
static void invokeChannelRegistered(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) {
//获取next的事件执行器,是相同线程就立即执行invokeChannelRegistered,不是提交任务执行;
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRegistered();
}
});
}
}
|
c.invokeChannelRegistered执行ChannelInboundHandler#channelRegistered
- 验证当前状态,完成或者等待添加执,执行ChannelInboundHandler#channelRegistered
- 发送异常,判断异常栈中没有方法名称等于exceptionCaught,就要调用ChannelInboundHandler.exceptionCaught
- 等于exceptionCaught,就是异常处理发送异常,不做处理
- 否,则往next查找执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private void invokeChannelRegistered() {
// 验证当前状态,完成或者等待添加执,执行ChannelInboundHandler#channelRegistered
// handlerState == ADD_COMPLETE || (!ordered && handlerState == ADD_PENDING);
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRegistered(this);//调用ChannelInboundHandler.channelRegistered
} catch (Throwable t) {
//判断异常栈中没有发现方法名称等于exceptionCaught,就要调用ChannelInboundHandler.exceptionCaught
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
fireChannelRegistered();//往下查找
}
}
|
(2).fireChannelActive() 触发next的Channel激活(TCP链路建立成功)事件;
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同
(3).fireChannelRead(Object) 触发next的读事件
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
1
2
3
4
5
|
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
//用于对象泄露,以及msg对null验证
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
...
}
|
(4).fireChannelReadComplete() 触发next的读操作完成通知事件;
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
(5).fireUserEventTriggered(Object) 用户自定义事件
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
1
2
3
4
5
|
static void invokeUserEventTriggered(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, final Object event) {
//验证事件内容不能为NULL
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(event, "event");
...
}
|
(6).fireChannelWritabilityChanged() Channel的可写状态变化通知事件;
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
(7).fireChannelInactive() TCP连接关闭,链路不可用通知事件。
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
(8).fireChannelUnregistered() 注销事件
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
(9).fireExceptionCaught(Throwable) 异常通知事件;
处理步骤跟findContextInbound一样,只是调用方法不同;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireExceptionCaught(final Throwable cause) {
invokeExceptionCaught(next, cause);
return this;
}
static void invokeExceptionCaught(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, final Throwable cause) {
//验证异常内容不能为NULL
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(cause, "cause");
...
}
|
6.Outbound事件
除flush和read方法,参数都有ChannelPromise,因为实现异步,所以类似回调方式,就引用ChannelPromise;
调用到Channel#Unsafe,成功或者失败都是异步处理ChannelPromise类;
(1).bind(SocketAddress, ChannelPromise) 绑定
执行步骤
- 验证ChannelPromise是否有效
- 往上查找Outbound事件的ChannelHandlerContext
- 获取事件执行器,是当前线程立即执行invokeBind,否,往事件执行器提交任务执行invokeBind;
- invokeBind方法就是调用ChannelOutboundHandler#bind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
//验证ChannelPromise
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {//验证promise
// cancelled
return promise;
}
//往上查找Outbound事件
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
//获取事件执行器,是当前线程立即执行invokeBind,否,往事件执行器提交任务执行invokeBind;
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null);
}
return promise;
}
|
a.isNotValidPromise 验证ChannelPromise是否有效
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
private boolean isNotValidPromise(ChannelPromise promise, boolean allowVoidPromise) {
if (promise == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("promise");
}
if (promise.isDone()) {
// 检查promise是否已取消,如果已取消,则表明不应执行该操作的处理。
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2349
if (promise.isCancelled()) {
return true;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("promise already done: " + promise);
}
if (promise.channel() != channel()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"promise.channel does not match: %s (expected: %s)", promise.channel(), channel()));
}
if (promise.getClass() == DefaultChannelPromise.class) {
return false;
}
if (!allowVoidPromise && promise instanceof VoidChannelPromise) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
StringUtil.simpleClassName(VoidChannelPromise.class) + " not allowed for this operation");
}
if (promise instanceof AbstractChannel.CloseFuture) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
StringUtil.simpleClassName(AbstractChannel.CloseFuture.class) + " not allowed in a pipeline");
}
return false;
}
|
b.findContextOutbound 往上查找Outbound事件的ChannelHandlerContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.prev;
} while (!ctx.outbound);
return ctx;
}
|
d.invokeBind方法就是调用ChannelOutboundHandler#bind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (invokeHandler()) {//上面Inbound事件说明过,判断状态是否添加或者等待添加
try {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);//调用ChannelOutboundHandler.bind
} catch (Throwable t) {
//promise#tryFailure
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
} else {
bind(localAddress, promise);//往上找
}
}
|
(2).connect(SocketAddress, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise)
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同;
(3).write
- write(Object msg)最终调用下面方法,自动生成DefaultChannelPromise对象
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return write(msg, newPromise());//DefaultChannelPromise
}
|
- write(final Object msg, final ChannelPromise promise)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(final Object msg, final ChannelPromise promise) {
//验证消息写入消息不能为NULL
if (msg == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("msg");
}
try {
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, true)) {//验证promise
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); //释放msg
// cancelled
return promise;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
//释放msg
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
throw e;
}
write(msg, false, promise);
return promise;
}
|
a.write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) flush为true做刷新数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();//往上查找
//内存泄漏检测
final Object m = pipeline.touch(msg, next);
//获取事件执行器,是当前线程立即执行invokeWriteAndFlush或者invokeWrite,否,往事件执行器提交任务执行invokeWriteAndFlush或者invokeWrite;
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
if (flush) {
//调用ChannelOutboundHandler#write
//调用ChannelOutboundHandler#flush
next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);
} else {
//调用ChannelOutboundHandler#write
next.invokeWrite(m, promise);
}
} else {
AbstractWriteTask task;
if (flush) {
task = WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
} else {
task = WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
}
//发送异常,调用ReferenceCountUtil.release
safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m);//自己定义executor执行任务
}
}
|
b.自定义Execute执行WriteAndFlushTask和WriteTask源码
WriteAndFlushTask和WriteTask实现AbstractWriteTask抽象类;
1).AbstractWriteTask源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
abstract static class AbstractWriteTask implements Runnable {
//是否估算内容大小
private static final boolean ESTIMATE_TASK_SIZE_ON_SUBMIT =
SystemPropertyUtil.getBoolean("io.netty.transport.estimateSizeOnSubmit", true);
// Assuming a 64-bit JVM, 16 bytes object header, 3 reference fields and one int field, plus alignment
//假设有一个64位的JVM, 16个字节的对象头,3个引用字段和一个int字段,加上对齐。
private static final int WRITE_TASK_OVERHEAD =
SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.transport.writeTaskSizeOverhead", 48);
private final Recycler.Handle<AbstractWriteTask> handle;//使用对象池
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx;
private Object msg;
private ChannelPromise promise;
private int size; //大小
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private AbstractWriteTask(Recycler.Handle<? extends AbstractWriteTask> handle) {
this.handle = handle;
}
protected static void init(AbstractWriteTask task, AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx,
Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
task.ctx = ctx;
task.msg = msg;
task.promise = promise;
if (ESTIMATE_TASK_SIZE_ON_SUBMIT) {
task.size = ctx.pipeline.estimatorHandle().size(msg) + WRITE_TASK_OVERHEAD;
ctx.pipeline.incrementPendingOutboundBytes(task.size);
} else {
task.size = 0;
}
}
@Override
public final void run() {
try {
// Check for null as it may be set to null if the channel is closed already
//如果通道已经关闭,则检查null,因为它可能被设置为null。
if (ESTIMATE_TASK_SIZE_ON_SUBMIT) {
ctx.pipeline.decrementPendingOutboundBytes(size);
}
write(ctx, msg, promise);
} finally {
// Set to null so the GC can collect them directly
ctx = null;
msg = null;
promise = null;
handle.recycle(this);
}
}
protected void write(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
ctx.invokeWrite(msg, promise);
}
}
|
2). WriteAndFlushTask源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
static final class WriteAndFlushTask extends AbstractWriteTask {
private static final Recycler<WriteAndFlushTask> RECYCLER = new Recycler<WriteAndFlushTask>() {
@Override
protected WriteAndFlushTask newObject(Handle<WriteAndFlushTask> handle) {
return new WriteAndFlushTask(handle);
}
}; //使用对象池
private static WriteAndFlushTask newInstance(
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
WriteAndFlushTask task = RECYCLER.get();
init(task, ctx, msg, promise);
return task;
}
private WriteAndFlushTask(Recycler.Handle<WriteAndFlushTask> handle) {
super(handle);
}
@Override
public void write(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
ctx.invokeFlush();//调用刷新
}
}
|
3). WriteTask源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
static final class WriteTask extends AbstractWriteTask implements SingleThreadEventLoop.NonWakeupRunnable {
private static final Recycler<WriteTask> RECYCLER = new Recycler<WriteTask>() {
@Override
protected WriteTask newObject(Handle<WriteTask> handle) {
return new WriteTask(handle);
}
};//使用对象池
private static WriteTask newInstance(
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
WriteTask task = RECYCLER.get();
init(task, ctx, msg, promise);
return task;
}
private WriteTask(Recycler.Handle<WriteTask> handle) {
super(handle);
}
}
|
(4).writeAndFlush(Object, ChannelPromise)
处理步骤跟write一样,Flush设置为true
(5).flush()
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同,不用处理ChannelPromise
(6).read()
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同,不用处理ChannelPromise
(7).disconnect(ChannelPromise)
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
@Override
public ChannelFuture disconnect() {
return disconnect(newPromise());
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture disconnect(final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
// Translate disconnect to close if the channel has no notion of disconnect-reconnect.
// So far, UDP/IP is the only transport that has such behavior.
//如果通道没有断开连接 - 重新连接的概念,则将断开连接转换为关闭状态。 到目前为止,UDP / IP是唯一具有这种行为的传输方式。
if (!channel().metadata().hasDisconnect()) {
next.invokeClose(promise);
} else {
next.invokeDisconnect(promise);
}
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!channel().metadata().hasDisconnect()) {
next.invokeClose(promise);
} else {
next.invokeDisconnect(promise);
}
}
}, promise, null);
}
return promise;
}
|
(8).close(ChannelPromise)
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同
(9).deregister(ChannelPromise)
处理步骤跟bind一样,只是调用方法不同
4.状态修改,CAS修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
final void setRemoved() {
handlerState = REMOVE_COMPLETE;
}
final void setAddComplete() {
for (;;) {
int oldState = handlerState;
// Ensure we never update when the handlerState is REMOVE_COMPLETE already.
// oldState is usually ADD_PENDING but can also be REMOVE_COMPLETE when an EventExecutor is used that is not
// exposing ordering guarantees.
if (oldState == REMOVE_COMPLETE || HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, oldState, ADD_COMPLETE)) {
return;
}
}
}
final void setAddPending() {
boolean updated = HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, INIT, ADD_PENDING);
assert updated; // This should always be true as it MUST be called before setAddComplete() or setRemoved().
}
|
5.DefaultChannelHandlerContext源码分析
ChannelPipeline添加ChannelHandler任务处理时,创建DefaultChannelHandlerContext拼接;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
final class DefaultChannelHandlerContext extends AbstractChannelHandlerContext {
private final ChannelHandler handler; //添加ChannelHandler属性
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(
DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(pipeline, executor, name, isInbound(handler), isOutbound(handler));
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handler");
}
this.handler = handler;
}
@Override
public ChannelHandler handler() {
return handler;
}
private static boolean isInbound(ChannelHandler handler) {
return handler instanceof ChannelInboundHandler;
}
private static boolean isOutbound(ChannelHandler handler) {
return handler instanceof ChannelOutboundHandler;
}
}
|
6.HeadContext源码分析
- HeadContext中Outbound事件底层都是Unsafe对象去调用;
- Inbound事件都都调用next,这里触发点;
- Inbound事件特殊处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
final class HeadContext extends AbstractChannelHandlerContext
implements ChannelOutboundHandler, ChannelInboundHandler {
private final Unsafe unsafe;
HeadContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline) {
super(pipeline, null, HEAD_NAME, false, true);
unsafe = pipeline.channel().unsafe();
setAddComplete();
}
@Override
public void read(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
unsafe.beginRead();
}
...
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();//触发等待添加任务
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelUnregistered();
//如果通道关闭且未注册,则按顺序删除所有处理程序。调用destroy
if (!channel.isOpen()) {
destroy();
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelReadComplete();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
private void readIfIsAutoRead() {
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();
}
}
...
}
|
7.TailContext源码分析
TailContext只实现Inbound事件,主要作用在于资源释放;channelRead
四、ChannelHandler 分析
1.ChannelHandler接口源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public interface ChannelHandler {
//ChannelPipeline添加ChannelHandler成功,回调通知方法
void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
//ChannelPipeline添加ChannelHandler删除,回调通知方法
void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
//过时,把这个方法移到ChannelInboundHandler接口中
@Deprecated
void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception;
/**
* 相同实例可以多次添加到一个或多个{ChannelPipeline},而不存在竞争条件。
*/
@Inherited
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Sharable {
// no value
}
}
|
ChannelHandler被注解为@Sharable,全局只有一个handler实例,它会被多个Channel的Pipeline共享,在被多线程并发时,不存在竞争条件;
2.ChannelHandlerAdapter抽象类源码分析
(1).属性
1
2
3
4
5
|
public abstract class ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelHandler {
// Not using volatile because it's used only for a sanity check.
//不要使用volatile,因为它只用于完整性检查。
boolean added;
|
(2).isSharable 判断类注解@Sharable
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public boolean isSharable() {
Class<?> clazz = getClass();
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> cache = InternalThreadLocalMap.get().handlerSharableCache();
Boolean sharable = cache.get(clazz);
if (sharable == null) {
sharable = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Sharable.class);
cache.put(clazz, sharable);//缓存InternalThreadLocalMap中;
}
return sharable;
}
|
3.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter类源码分析
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter类的UML
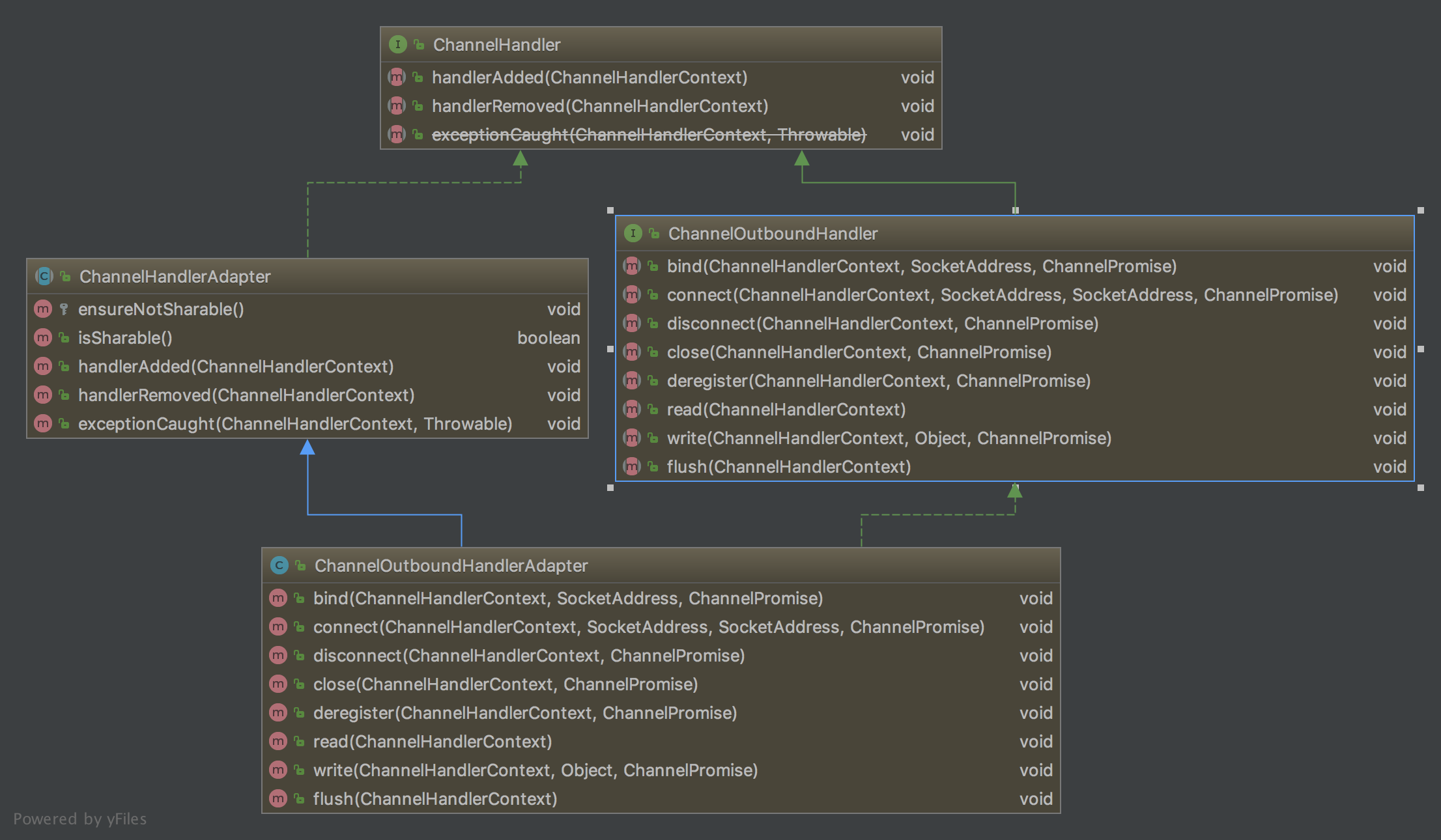
ChannelOutboundHandler的Outbound事件方法调用ChannelHandlerContext方法;
4.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter类源码分析
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter类的UML
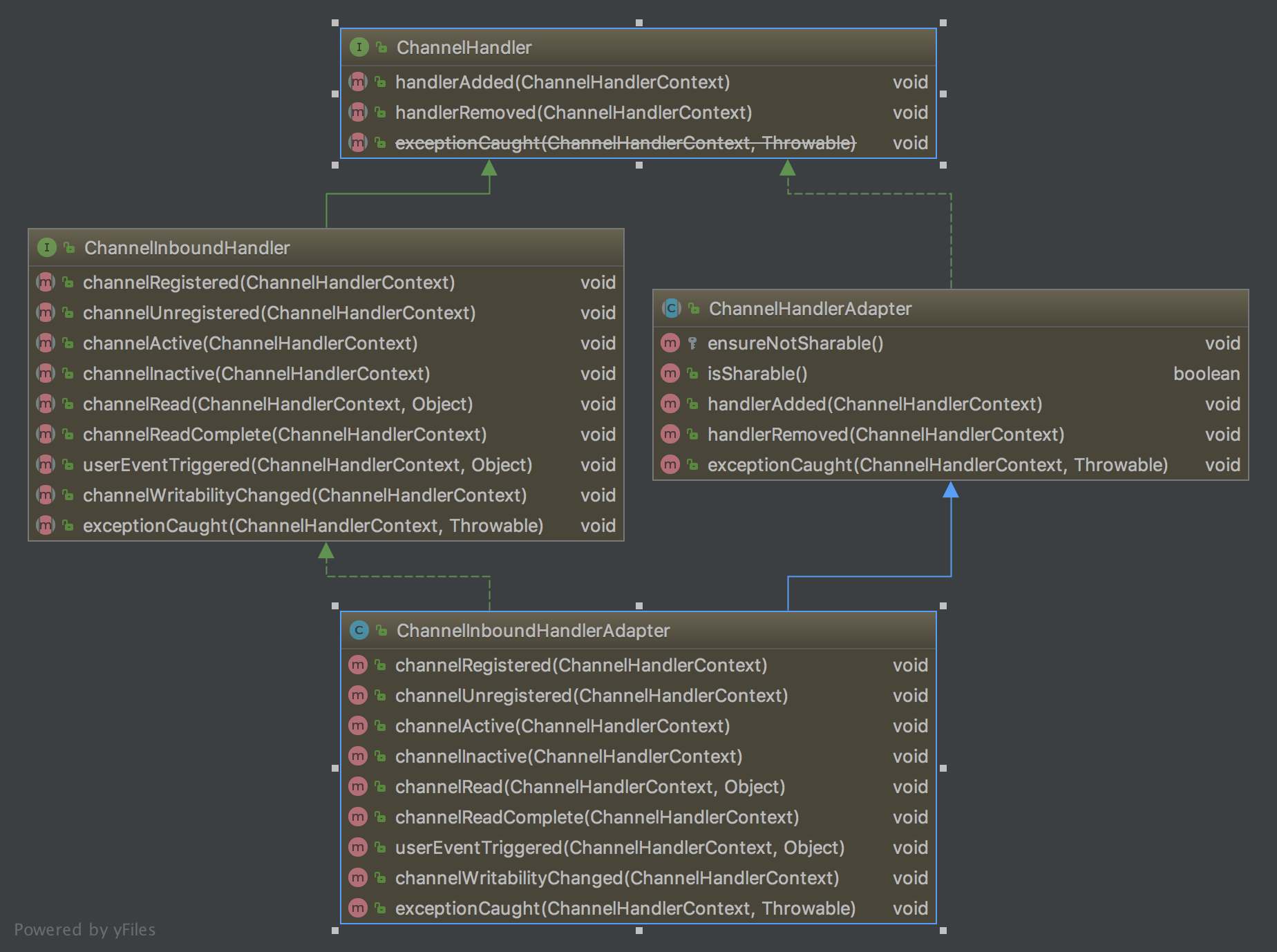
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的Inbound事件调用ChannelHandlerContext方法;
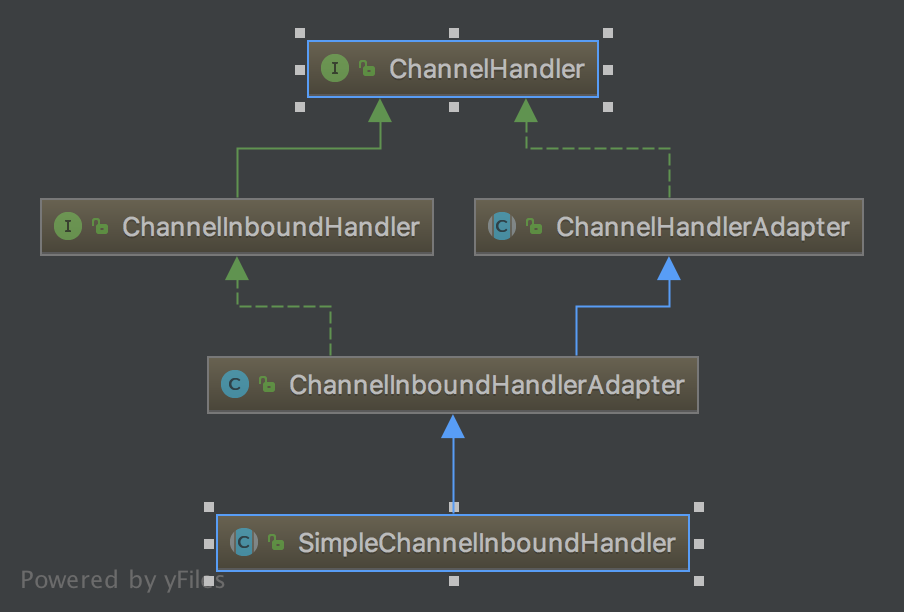
5.SimpleChannelInboundHandler 允许显式只处理特定类型的消息
SimpleChannelInboundHandler类的UML
(1).属性
1
2
3
4
5
|
public abstract class SimpleChannelInboundHandler<I> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private final TypeParameterMatcher matcher;//类型参数匹配器
private final boolean autoRelease; //自动释放资源
}
|
(2).channelRead
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
boolean release = true;
try {
if (acceptInboundMessage(msg)) { //类型判断
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I imsg = (I) msg;
channelRead0(ctx, imsg);//抽象方法,子类实现
} else {
release = false;
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); //手动触发查找next的channelRead
}
} finally {
if (autoRelease && release) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
}
|
五、总结
1.Channelpipeline是线程安全?
ChannelPipeline执行ChannelHandler连时,先判断AbstractChannelHandlerContext中事件执行器是否当前线程,是立即执行,不是提交任务执行ChannelHandler;
导致只有单线程执行ChannelHandler;保障线程是安全;
head没有制定事件执行器,还是用channel的事件执行器,说明在Outbound事件时,channel的事件执行器,不存在多线程处理;线程安全;
2.Channelpipeline执行流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
* I/O Request
* Channel.writeAndFlush
* |
* +---------------------------------------------------+--------------------+
* | ChannelPipeline |writeAndFlush |
* | \|/ |
* | +---------------------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | | Inbound channelRead tail | | Outbound writeAndFlush tail| |
* | +----------+----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | /|\ | writeAndFlush |
* | |fireChannelRead \|/ |
* | +----------+----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | | Inbound channelRead next | | Outbound writeAndFlush prev| |
* | +----------+----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | /|\ . writeAndFlush |
* | . . |
* | . . |
* | . fireChannelRead \|/ |
* | +----------+-----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | | Inbound channelRead next | | Outbound writeAndFlush prev| |
* | +----------+-----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | /|\ | writeAndFlush |
* | | fireChannelRead \|/ |
* | +----------+-----------------+ +------------+------------ --+ |
* | | Inbound channelRead head | | Outbound writeAndFlush prev| |
* | +----------+-----------------+ +------------+---------------+ |
* | /|\ | flush |
* +---------------+-----------------------------------+--------------------+
* |fireChannelRead \|/
* +---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
* | | | |
* | [ Socket.read() ] [ Socket.write() ] |
* | |
* | Netty Internal I/O Threads (Transport Implementation) |
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------+
*
|
写ChannelHandler自己手动触发next(fire开头名称)Inbound事件或者prev(write,bind…)Outbound事件





