【注意】最后更新于 March 17, 2019,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
一、介绍
Channel是 Netty抽象出来的网络I/O读写相关的接口,为什么不使用JDK NIO原生的Channel而要另起炉灶呢
主要原因如下:
-
(1)JDK的Socketchannel和ServerSocketchannel没有统一的Channel接口供业务开发者使用,对于用户而言,没有统一的API操作,使用起来并不方便。
-
(3) Netty的Channel需要能够跟Netty的整体架构融合在一起,例如I/O模型、基于Channelpipeline的定制模型,以及基于元数据描述配置化的TCP参数等,
这些JDK的Socketchannel和 Serversocketchannel都没有提供,需要重新封装;
-
(4)自定义的 Channel,功能实现更加灵活。
基于上述4个原因,Nety重新设计了Channel接口,并且给予了很多不同的实现。它的设计原理比较简单,但是功能却比较繁杂,主要的设计理念如下。
-
(1)在Channel接口层,采用Facade模式进行统一封装,将网络I/O操作、网络IO相关联的其他操作封装起来,统一对外提供。
-
(2) Channel接口的定义尽量大而全,为 Socketchannel和 ServerSocketchannel提供统一的规范,由不同子类实现不同的功能,公共功能在抽象父类中实现,最大程度地实现功能和接口的重用
-
(3)具体实现采用聚合而非包含的方式,将相关的功能类聚合在 Channel中,由 Channel统一负责分配和调度,功能实现更加灵活。
二、Channel接口说明
Channel接口方法如图下:
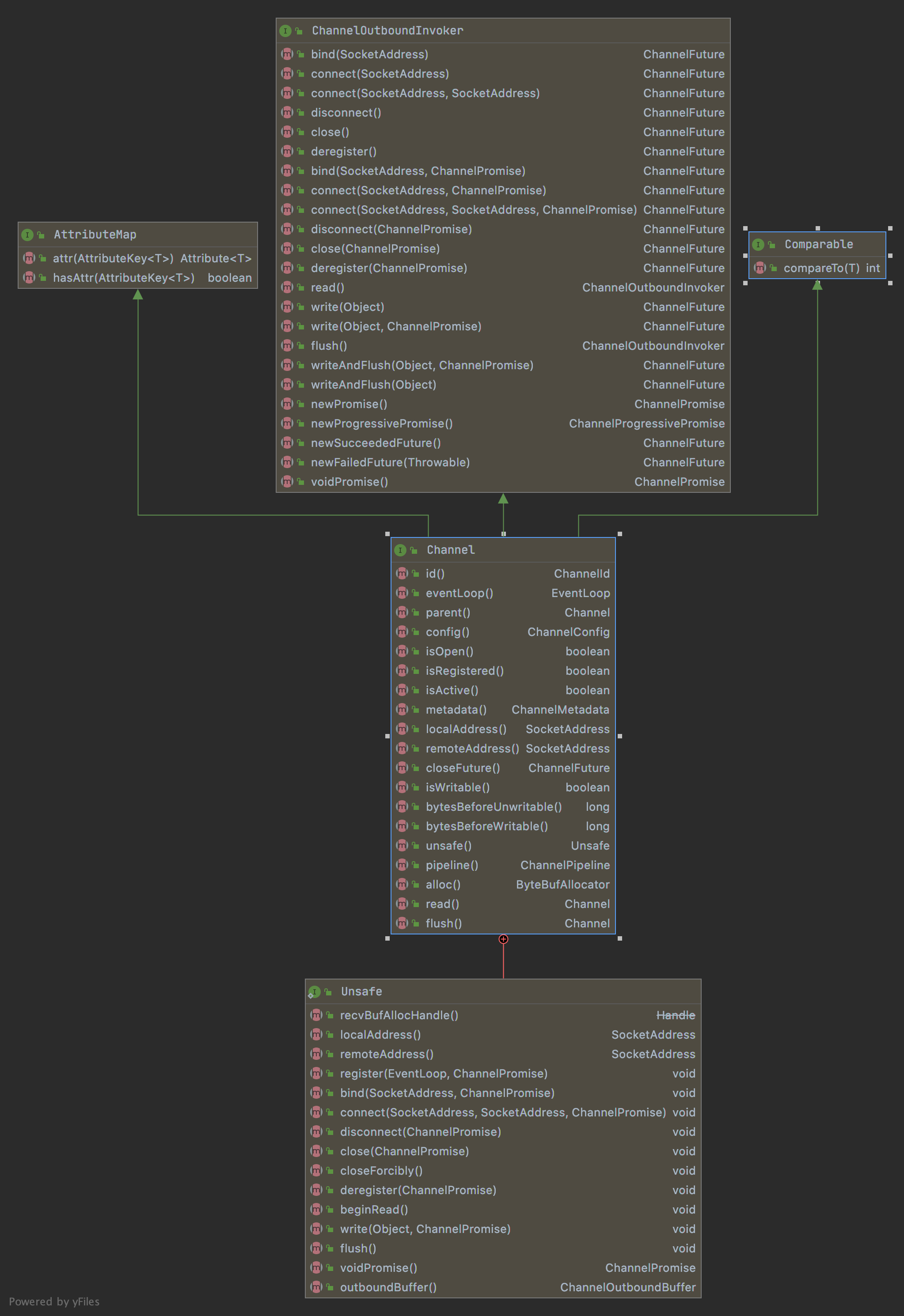
Channel接口中有个Unsafe接口;Unsafe接口实际上是 Channel接口的辅助接口,它不应该被用户代码直接调用。实际
的I/O读写操作都是由Unsafe接口负责完成的
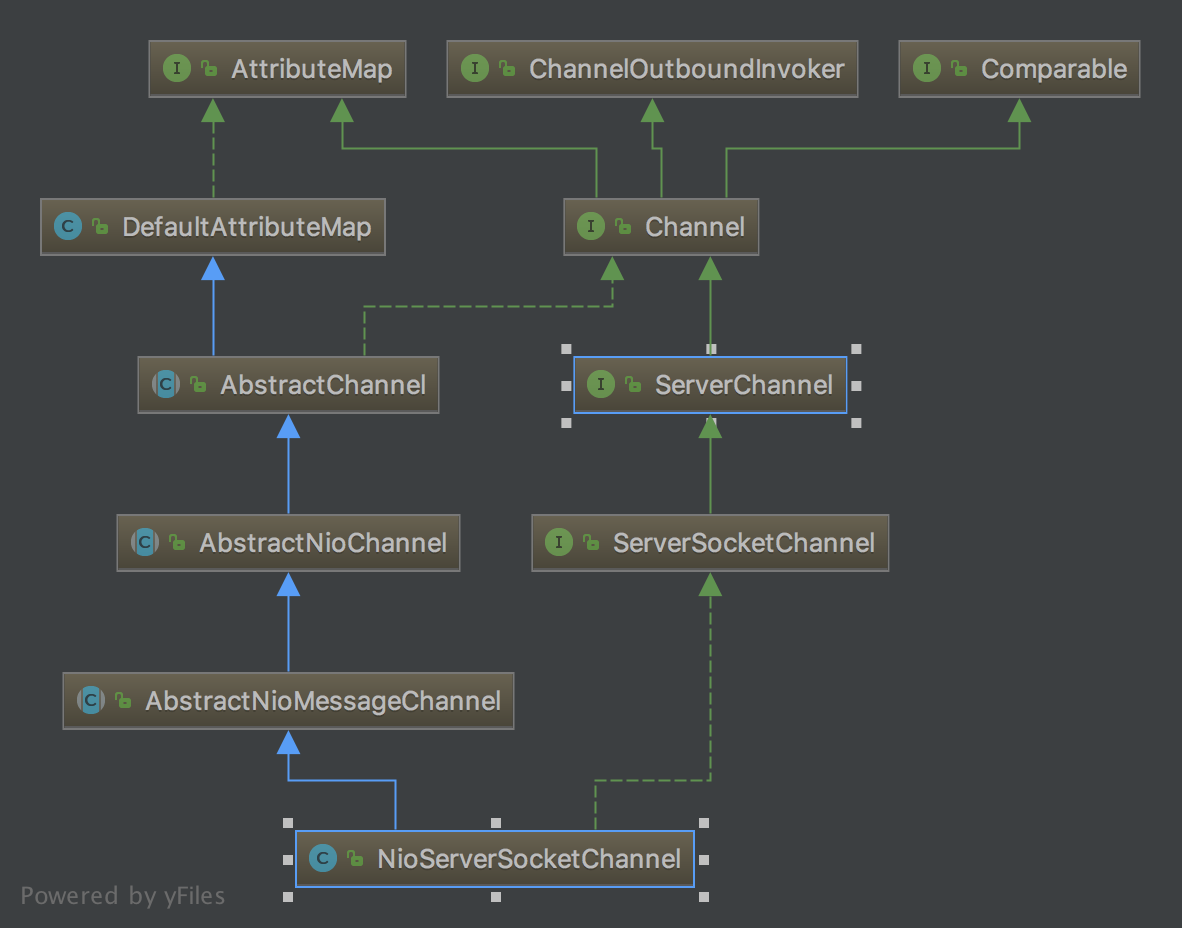
Channel接口实现子类很多,主要讲解NioServerSocketChannel和NioSocketChannel两个类;
NioServerSocketChannel类UML图
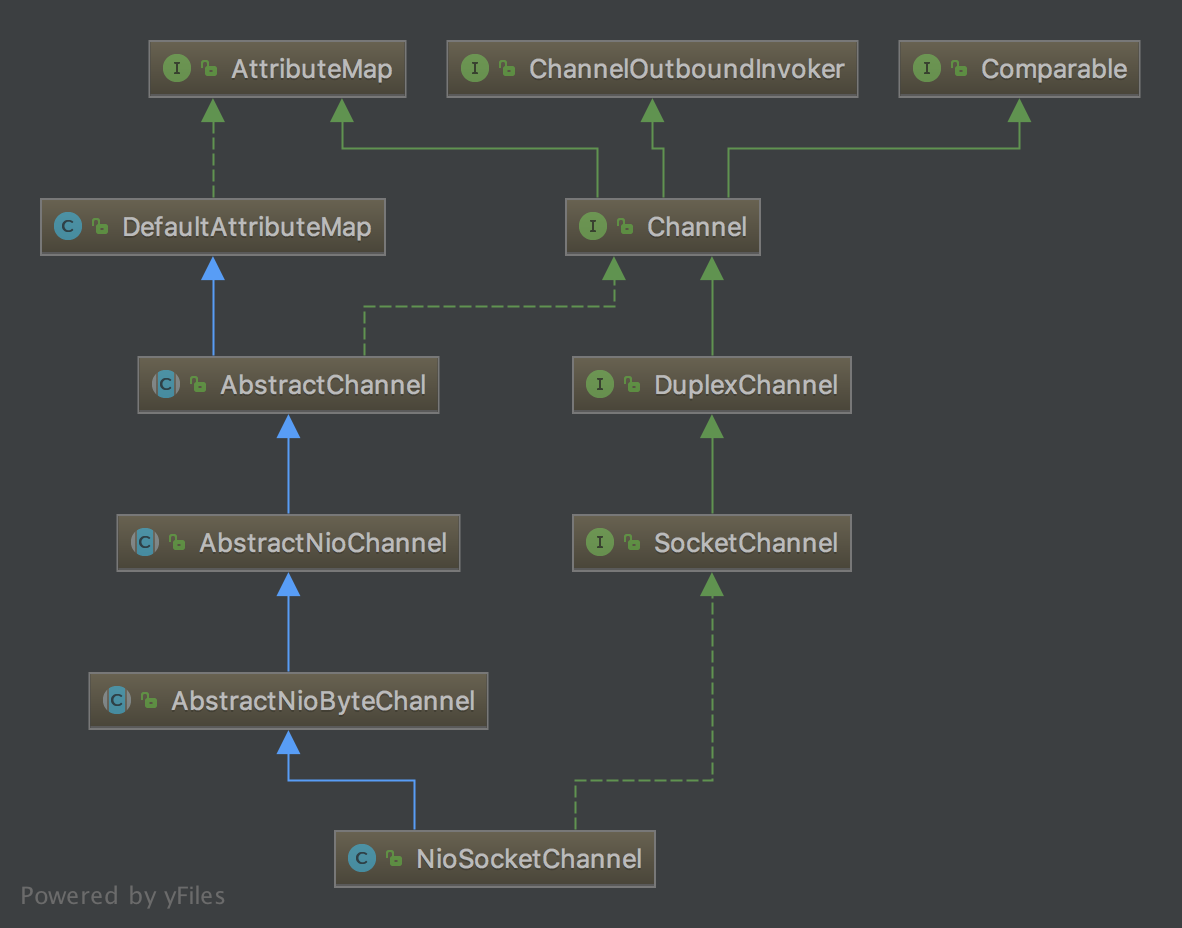
NioSocketChannel类UML图
三、AbstractChannel源码分析
1.属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public abstract class AbstractChannel extends DefaultAttributeMap implements Channel {
//父Channel 在NIO 用于服务端accept创建NioSocketChannel自定父类
private final Channel parent;
private final ChannelId id; //采用默认方式生成的全局唯一ID;
private final Unsafe unsafe; //Unsafe
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline; //当前Channel对应DefaultChannelPipeline
private final VoidChannelPromise unsafeVoidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(this, false);
private final CloseFuture closeFuture = new CloseFuture(this);
private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;//本地地址
private volatile SocketAddress remoteAddress;//远程地址
private volatile EventLoop eventLoop; //当前Channel注册EventLoop
private volatile boolean registered; //注册状态
private boolean closeInitiated; //关闭初始化状态
/** Cache for the string representation of this channel */
//缓存此通道的字符串表示形式
private boolean strValActive;
private String strVal;
}
|
2.构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe(); //抽象方法,子类去实现
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent, ChannelId id) {
this.parent = parent;
this.id = id;
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
|
- 主要职责创建DefaultChannelPipeline
3.bind,connect,disconnect,close,read,writed等这些方法都是委托pipeline实现滴;
4.localAddress,remoteAddress方法都是由Unsafe对象去实现
5.AbstractUnsafe源码分析
(1).属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
protected abstract class AbstractUnsafe implements Unsafe {
private final ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = new ChannelOutboundBuffer(AbstractChannel.this);
private RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle recvHandle;
private boolean inFlush0;
/** true if the channel has never been registered, false otherwise */
//如果通道从未被注册,则返回true,否则返回false
private final boolean neverRegistered = true;
}
|
(2).register只要创建Channel,第一件事就要调用register方法;
主要处理的步骤:
- EventLoop赋值操作,异步执行调用EventLoop执行,ChannelPromise也是异步提交
- 调用doRegister()空方法
- pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded()添加Channelhandler
- pipeline.fireChannelRegistered()
- 是否激活,是pipeline.fireChannelActive()
(3).beginRead
- pipeline.fireChannelActive()最终调用代码
1
2
3
|
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();==>最终调用beginRead
}
|
- doBeginRead抽象方法,子类做NIO事件监听操作
- NioSocketChannel对应OP_READ
- NioServerSocketChannel对应OP_ACCEPT
(4).bind 服务绑定端口操作抽象doBind方法子类实现
(5).disconnect 断开
- doDisconnect 抽象方法
- NioSocketChannel调用doClose
- NioServerSocketChannel不支持
- pipeline.fireChannelInactive()
(6).close
closeExecutor调度执行close,抽象doClose()方法;
(7).deregister
- 抽象doDeregister
- pipeline.fireChannelInactive();
- pipeline.fireChannelUnregistered()
(8).write
- 往ChannelOutboundBuffer添加消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
@Override
public final void write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null) { //channel关闭中,禁止写数据
// If the outboundBuffer is null we know the channel was closed and so
// need to fail the future right away. If it is not null the handling of the rest
// will be done in flush0()
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2362
safeSetFailure(promise, WRITE_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION);
// release message now to prevent resource-leak
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); //防止释放msg泄漏。
return;
}
int size;
try {
msg = filterOutboundMessage(msg);//过滤
//估算大小
size = pipeline.estimatorHandle().size(msg);
if (size < 0) {
size = 0;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return;
}
outboundBuffer.addMessage(msg, size, promise);//添加消息
}
|
(9).flush 真正往网络发送消息
抽象doWrite子类实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
@Override
public final void flush() {
assertEventLoop();
ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null) {//channel 关闭
return;
}
outboundBuffer.addFlush();// 添加一个刷新标记
flush0();
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void flush0() {
if (inFlush0) {
// Avoid re-entrance
return;
}
final ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null || outboundBuffer.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
inFlush0 = true;
// Mark all pending write requests as failure if the channel is inactive.
//如果channel非激活状态,将所有挂起的写请求标记为失败。
if (!isActive()) {
try {
if (isOpen()) {
outboundBuffer.failFlushed(FLUSH0_NOT_YET_CONNECTED_EXCEPTION, true);
} else {
// Do not trigger channelWritabilityChanged because the channel is closed already.
outboundBuffer.failFlushed(FLUSH0_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION, false);
}
} finally {
inFlush0 = false;
}
return;
}
try {
doWrite(outboundBuffer); //抽象方法
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (t instanceof IOException && config().isAutoClose()) {
/**
* Just call {@link #close(ChannelPromise, Throwable, boolean)} here which will take care of
* failing all flushed messages and also ensure the actual close of the underlying transport
* will happen before the promises are notified.
*
* This is needed as otherwise {@link #isActive()} , {@link #isOpen()} and {@link #isWritable()}
* may still return {@code true} even if the channel should be closed as result of the exception.
*/
close(voidPromise(), t, FLUSH0_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION, false);//写异常,就关闭
} else {
try {
shutdownOutput(voidPromise(), t);
} catch (Throwable t2) {
close(voidPromise(), t2, FLUSH0_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION, false);
}
}
} finally {
inFlush0 = false;
}
}
|
6.总结
- 封装异常处理,提供抽象方法,让子类处理相关的业务
- ChannelOutboundBuffer处理写操作
- connect和read未实现,子类实现
四、AbstractNioChannel源码分析
1.属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public abstract class AbstractNioChannel extends AbstractChannel {
private final SelectableChannel ch; //包装的JDK Channel
protected final int readInterestOp; //Read事件,服务端OP_ACCEPT,其他OP_READ
volatile SelectionKey selectionKey; //对应JDK SelectionKey
boolean readPending; //底层读事件进行标记
//清除readPending标记
private final Runnable clearReadPendingRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
clearReadPending0();
}
};
}
|
2.doRegister
获取Java的SelectionKey;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
...
}
}
|
4.doDeregister
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
protected void doDeregister() throws Exception {
eventLoop().cancel(selectionKey());//eventLoop处理取消
}
|
5.doBeginRead 设置当前监听事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) { //选择键被取消而不再有效
return;
}
readPending = true; //设置底层读事件
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
//读事件设置
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
|
6.doClose
啥没处理,子类重写这个方法
7.AbstractNioUnsafe源码分析
1
|
protected abstract class AbstractNioUnsafe extends AbstractUnsafe implements NioUnsafe
|
(1).实现NioUnsafe接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
/**
* Special {@link Unsafe} sub-type which allows to access the underlying {@link SelectableChannel}
*/
public interface NioUnsafe extends Unsafe {
/**
* Return underlying {@link SelectableChannel}
*/
SelectableChannel ch();
/**
* 客户端链接服务端成功,调用finishConnect
*/
void finishConnect();
/**
* Read from underlying {@link SelectableChannel}
*/
void read();
//立即强制刷新
void forceFlush();
}
|
(2).connect 链接服务端
- doConnect抽象方法
- pipeline().fireChannelActive();
(3).finishConnect
- doFinishConnect()抽象方法
- pipeline().fireChannelActive();
(4).flush0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@Override
protected final void flush0() {
//只有在没有等待刷新时立即刷新。如果有一个待定的刷新操作,事件循环将调用forceFlush(),因此现在不需要调用它。
if (isFlushPending()) {
return;
}
super.flush0();
}
private boolean isFlushPending() {
SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKey();
//OP_WRITE表示通道可写
return selectionKey.isValid() && (selectionKey.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0;
}
|
(4).forceFlush 立即强制刷新
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Override
public final void forceFlush() {
// 立即强制刷新
super.flush0();
}
|
(5).removeReadOp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
protected final void removeReadOp() {
SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
// Check first if the key is still valid as it may be canceled as part of the deregistration
// from the EventLoop
//首先检查键是否仍然有效,因为它可能会被取消,作为从EventLoop注销的一部分
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2104
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) != 0) {
// only remove readInterestOp if needed
//只需要删除readInterestOp
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~readInterestOp);
}
}
|
五、AbstractNioMessageChannel源码分析
服务端AbstractNioMessageChannel
2.doWrite
- doWriteMessage抽象方法
- NioServerSocketChannel不支持操作,主要充当ACCEPT,链接客服端角色;
3.NioMessageUnsafe 源码分析
1.属性
1
2
3
4
|
private final class NioMessageUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
private final List<Object> readBuf = new ArrayList<Object>();//doReadMessages用到这个集合
}
|
2.read读数据
- doReadMessages抽象方法
- NioServerSocketChannel实现就是客服端链接成功Channel
- 运用RecvByteBufAllocator
- pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));//触发ChannelRead事件
- pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
六、NioServerSocketChannel源码分析
1.构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public class NioServerSocketChannel extends AbstractNioMessageChannel
implements io.netty.channel.socket.ServerSocketChannel {
private static final ChannelMetadata METADATA = new ChannelMetadata(false, 16);
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
/**
* Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in
* {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each ServerSocketChannel.open() otherwise.
*
* See <a href="https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2308">#2308</a>.
*/
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
private final ServerSocketChannelConfig config;
/**
* Create a new instance
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
}
|
2.doBind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
|
3.doReadMessages 创建NioSocketChannel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
}...
return 0;
}
|
4.doClose
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
protected void doClose() throws Exception {
javaChannel().close();
}
|
七、AbstractNioByteChannel源码分析
1.构造
1
2
3
|
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
|
2.doWrite
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
//循环写次数,默认16次
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
// Wrote all messages.
clearOpWrite(); //清除SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
// Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called.
return;
}
writeSpinCount -= doWriteInternal(in, msg);
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
protected final void incompleteWrite(boolean setOpWrite) {
// IO写满了,设置SelectionKey.OP_WRITE事件
if (setOpWrite) {
setOpWrite();
} else { //writeSpinCount为零情况,数据没写完,提交eventLoop处理
// Schedule flush again later so other tasks can be picked up in the meantime
Runnable flushTask = this.flushTask;
if (flushTask == null) {
flushTask = this.flushTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
flush(); // pipeline.flush();
}
};
}
//flushTask任务提交eventLoop
eventLoop().execute(flushTask);
}
}
|
a.doWriteInternal 对不同类型写操作
- ByteBuf调用doWriteBytes抽象方法
- FileRegion调用doWriteFileRegion方法
- 写多少字节同步ChannelOutboundBuffer#progress
- 已经读完调用ChannelOutboundBuffer#remove
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
private int doWriteInternal(ChannelOutboundBuffer in, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
final int localFlushedAmount = doWriteBytes(buf);//抽象方法
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
in.progress(localFlushedAmount); //通知有关写入进度的当前消息的{@link ChannelPromise}。
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else if (msg instanceof FileRegion) {//FileRegion是Netty对NIO底层的FileChannel的封装
FileRegion region = (FileRegion) msg;
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
long localFlushedAmount = doWriteFileRegion(region);//模版方法
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else {
// Should not reach here.
throw new Error();
}
return WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL;
}
|
3.doWrite0 直接调用doWriteInternal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/**
* Write objects to the OS.
* 将对象写入操作系统。
* @param in the collection which contains objects to write.
* @return The value that should be decremented from the write quantum which starts at
* {@link ChannelConfig#getWriteSpinCount()}. The typical use cases are as follows:
* <ul>
* <li>0 - if no write was attempted. This is appropriate if an empty {@link ByteBuf} (or other empty content)
* is encountered</li>
* <li>1 - if a single call to write data was made to the OS</li>
* <li>{@link ChannelUtils#WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL} - if an attempt to write data was made to the OS, but no
* data was accepted</li>
* </ul>
* @throws Exception if an I/O exception occurs during write.
*/
protected final int doWrite0(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
// Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called.
return 0;
}
return doWriteInternal(in, in.current());
}
|
4.NioByteUnsafe 源码分析
(1).read
- RecvByteBufAllocator的实现类AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator构建一个最优大小的缓冲区来接收数据
- doReadBytes抽象方法
- pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf)
- pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
|
@Override
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();//allocHandle不为空情况config().getRecvByteBufAllocator().newHandle();
//重置统计信息
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
//获取读取大小
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));//doReadBytes抽象方法
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();//释放
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
//当我们收到EOF时,没有什么可以阅读的。
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);//触发ChannelRead事件,用户处理
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading()); //判断是否继续读取
//重新计算下次读取的大小
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
private void closeOnRead(ChannelPipeline pipeline) {
if (!isInputShutdown0()) { //默认是false
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.ALLOW_HALF_CLOSURE))) {
shutdownInput(); //抽象方法
pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownEvent.INSTANCE);
} else {
close(voidPromise());
}
} else {
pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownReadComplete.INSTANCE);
}
}
private void handleReadException(ChannelPipeline pipeline, ByteBuf byteBuf, Throwable cause, boolean close,
RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle) {
if (byteBuf != null) {
if (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
} else {
byteBuf.release();
}
}
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
if (close || cause instanceof IOException) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
}
|
八、NioSocketChannel源码分析
1.构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class NioSocketChannel extends AbstractNioByteChannel implements io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel {
private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(NioSocketChannel.class);
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
private static SocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
/**
* Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in
* {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each SocketChannel.open() otherwise.
*
* See <a href="https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2308">#2308</a>.
*/
return provider.openSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a socket.", e);
}
}
private final SocketChannelConfig config;
public NioSocketChannel() {
this(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER);
}
}
|
2.doConnect 链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@Override
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
if (!connected) {
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
|
4.doFinishConnect
1
2
3
4
5
|
protected void doFinishConnect() throws Exception {
if (!javaChannel().finishConnect()) {
throw new Error();
}
}
|
5.doReadBytes
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Override
protected int doReadBytes(ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead(byteBuf.writableBytes());
return byteBuf.writeBytes(javaChannel(), allocHandle.attemptedBytesRead());
}
|
6.doWriteBytes
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Override
protected int doWriteBytes(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception {
final int expectedWrittenBytes = buf.readableBytes();
return buf.readBytes(javaChannel(), expectedWrittenBytes);
}
|
7.doWriteFileRegion transferTo运用零CP
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Override
protected long doWriteFileRegion(FileRegion region) throws Exception {
final long position = region.transferred();
return region.transferTo(javaChannel(), position);
}
|
6.doWrite
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
//循环写次数,默认16次
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
if (in.isEmpty()) {
// All written so clear OP_WRITE
clearOpWrite();
// Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called.
return;
}
// Ensure the pending writes are made of ByteBufs only.
//确保挂起写入操作仅由ByteBufs组成。
int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite();
ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount();
// Always us nioBuffers() to workaround data-corruption.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2761
switch (nioBufferCnt) {
case 0:
// We have something else beside ByteBuffers to write so fallback to normal writes.
//除了ByteBuffers之外,FileRegion正常的写入。
writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in);
break;
case 1: {
// Only one ByteBuf so use non-gathering write
// Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need
// to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero.
//只有一个ByteBuf使用非收集写入零长度缓冲区不会被ChannelOutboundBuffer添加到nioBuffers,因此不需要检查所有缓冲区的总大小是否非零。
ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0];
int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining();
final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer);
if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) {
incompleteWrite(true);
return;
}
//每次调整写入的最大字节数
adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes);
--writeSpinCount;
break;
}
default: {
// Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need
// to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero.
// We limit the max amount to int above so cast is safe
//零长度缓冲区不会被ChannelOutboundBuffer添加到nioBuffers,所以不需要检查所有缓冲区的总大小是否非零。
// 我们把最大的数量限制在int以上,所以cast是安全的
long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize();
final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt);
if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) {
incompleteWrite(true);
return;
}
// Casting to int is safe because we limit the total amount of data in the nioBuffers to int above.
//每次调整写入的最大字节数
adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes,
maxBytesPerGatheringWrite);
in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes);
--writeSpinCount;
break;
}
}
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
|
a.每次调整写入的最大字节数(adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite)
优点:
- 尽可能地根据操作系统行为的变化进行调整;
- 组装大的内容,不要分多个批次,提高点性能;
处理逻辑:
- 预计写的字节大小跟已写的字节数相同,设置为预计处理的两倍
- 预计写的字节大小大于4096且预计写的字节的一半大于已写的字节数相同,设置为预计处理的一半
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private void adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(int attempted, int written, int oldMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite) {
// By default we track the SO_SNDBUF when ever it is explicitly set. However some OSes may dynamically change
// SO_SNDBUF (and other characteristics that determine how much data can be written at once) so we should try
// make a best effort to adjust as OS behavior changes.
//默认情况下,我们跟踪SO_SNDBUF,当它明确设置。然而,一些操作系统可能会动态地改变SO_SNDBUF(以及其他决定可以一次写入多少数据的特性)
// ,所以我们应该尽可能地根据操作系统行为的变化进行调整。
// 预计写的字节大小跟已写的字节数相同,设置为预计处理的两倍
if (attempted == written) {
if (attempted << 1 > oldMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite) {
((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).setMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attempted << 1);
}
// 4096
// 预计写的字节大小大于4096且预计写的字节的一半大于已写的字节数相同,设置为预计处理的一半
} else if (attempted > MAX_BYTES_PER_GATHERING_WRITE_ATTEMPTED_LOW_THRESHOLD && written < attempted >>> 1) {
((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).setMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attempted >>> 1);
}
}
|
九、ChannelOutboundBuffer
写的缓冲区,调用write时候,只是把发送消息添加到ChannelOutboundBuffer缓冲区,调用flush真正发送
1.内部数据结构
1
2
3
|
private Entry flushedEntry; // flush 开始第一个节点,Entry是链表
private Entry unflushedEntry;// 被添加的开始节点,但没有准备好被消费。
private Entry tailEntry;// 最后一个节点,添加
|
三个对象变量的处理逻辑,write调用addMessage方法的时候,创建Entry将这个Entry追加到TailEntry节点后面;unflushedEntry为空把当前赋值给unflushedEntry;
flush调用addFlush的时候,将unflushedEntry的引用赋给flushedEntry,然后将unflushedEntry置为null。
2.addMessage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public void addMessage(Object msg, int size, ChannelPromise promise) {
Entry entry = Entry.newInstance(msg, size, total(msg), promise);
if (tailEntry == null) {
flushedEntry = null;
tailEntry = entry;
} else {
Entry tail = tailEntry;
tail.next = entry;
tailEntry = entry;
}
if (unflushedEntry == null) {
unflushedEntry = entry;
}
// increment pending bytes after adding message to the unflushed arrays.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1619
incrementPendingOutboundBytes(entry.pendingSize, false);
}
|
(1).写一直写下去,不调用调用Flush,发生OOM;
unwritable变量控制fireChannelWritabilityChanged事件;用户自己实现这块,控制write频率;
a.incrementPendingOutboundBytes 写的缓冲区大于写的缓冲区的高水位就修改unwritable变量
- getWriteBufferHighWaterMark 写的缓冲区的高水位,默认64k
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private void incrementPendingOutboundBytes(long size, boolean invokeLater) {
if (size == 0) {
return;
}
long newWriteBufferSize = TOTAL_PENDING_SIZE_UPDATER.addAndGet(this, size);
if (newWriteBufferSize > channel.config().getWriteBufferHighWaterMark()) {
setUnwritable(invokeLater);
}
}
|
(2).写的缓冲区的高水位降下去,有没有通知我加快write频率呢?肯定有,这个就是所谓写的缓冲区的低水位,这样会触发fireChannelWritabilityChanged
删除(remove)写缓存记录是调用decrementPendingOutboundBytes,控制缓冲区低水位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
private void decrementPendingOutboundBytes(long size, boolean invokeLater, boolean notifyWritability) {
if (size == 0) {
return;
}
long newWriteBufferSize = TOTAL_PENDING_SIZE_UPDATER.addAndGet(this, -size);
if (notifyWritability && newWriteBufferSize < channel.config().getWriteBufferLowWaterMark()) {
setWritable(invokeLater);
}
}
|
3.addFlush
动机把unflushedEntry赋值给flushedEntry;DefaultChannelPipeline在做inEventLoop验证,不存在并发写;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public void addFlush() {
// There is no need to process all entries if there was already a flush before and no new messages
// where added in the meantime.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2577
Entry entry = unflushedEntry;
if (entry != null) {
//动机可以控制一边写一边flushed,上一批没写完,没关系,Entry是链表往下查找;
if (flushedEntry == null) {
// there is no flushedEntry yet, so start with the entry
flushedEntry = entry;
}
do {
//验证entry是否取消动作
flushed ++;
if (!entry.promise.setUncancellable()) {
// Was cancelled so make sure we free up memory and notify about the freed bytes
int pending = entry.cancel();
decrementPendingOutboundBytes(pending, false, true);
}
entry = entry.next;
} while (entry != null);
// All flushed so reset unflushedEntry
unflushedEntry = null;
}
}
|
4.Entry结构
运用对象池;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
static final class Entry {
private static final Recycler<Entry> RECYCLER = new Recycler<Entry>() {
@Override
protected Entry newObject(Handle<Entry> handle) {
return new Entry(handle);
}
};
private final Handle<Entry> handle;
Entry next;
Object msg;
//这个NIO转化ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer[] bufs;
ByteBuffer buf;
ChannelPromise promise;
long progress;
long total;
int pendingSize;
int count = -1;
boolean cancelled;
}
|
1.创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
static Entry newInstance(Object msg, int size, long total, ChannelPromise promise) {
Entry entry = RECYCLER.get();
entry.msg = msg;
// CHANNEL_OUTBOUND_BUFFER_ENTRY_OVERHEAD:96,
entry.pendingSize = size + CHANNEL_OUTBOUND_BUFFER_ENTRY_OVERHEAD;
entry.total = total;
entry.promise = promise;
return entry;
}
|
a.pendingSize加96,96是啥呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// Assuming a 64-bit JVM:
// - 16 bytes object header
// - 8 reference fields ==>改成 6 reference fields
// - 2 long fields
// - 2 int fields
// - 1 boolean field ==> 4bytes
// - padding
|
6.nioBuffers 提供这个,主要NIO的写必须用ByteBuf转化ByteBuffer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
public ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers(int maxCount, long maxBytes) {
assert maxCount > 0;
assert maxBytes > 0;
long nioBufferSize = 0;
int nioBufferCount = 0;
final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = NIO_BUFFERS.get(threadLocalMap);
Entry entry = flushedEntry;
while (isFlushedEntry(entry) && entry.msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
if (!entry.cancelled) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) entry.msg;
final int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex();
final int readableBytes = buf.writerIndex() - readerIndex;
if (readableBytes > 0) {
if (maxBytes - readableBytes < nioBufferSize && nioBufferCount != 0) {
// If the nioBufferSize + readableBytes will overflow maxBytes, and there is at least one entry
// we stop populate the ByteBuffer array. This is done for 2 reasons:
// 1. bsd/osx don't allow to write more bytes then Integer.MAX_VALUE with one writev(...) call
// and so will return 'EINVAL', which will raise an IOException. On Linux it may work depending
// on the architecture and kernel but to be safe we also enforce the limit here.
// 2. There is no sense in putting more data in the array than is likely to be accepted by the
// OS.
// 如果nioBufferSize + readableBytes将溢出maxBytes,并且至少存在一个条目,我们将停止填充ByteBuffer数组。这样做有两个原因:
// 1. bsd / osx不允许通过一次writev(...)调用写入更多字节,然后是Integer.MAX_VALUE,因此将返回'EINVAL',这将引发IOException。
// 在Linux上,它可能会根据体系结构和内核而起作用,但是为了安全起见,我们在此处也施加了限制。
// 2.在阵列中放入比操作系统可能接受的更多的数据没有任何意义
// See also:
// - https://www.freebsd.org/cgi/man.cgi?query=write&sektion=2
// - http://linux.die.net/man/2/writev
break;
}
nioBufferSize += readableBytes;
int count = entry.count;
if (count == -1) {
//noinspection ConstantValueVariableUse
entry.count = count = buf.nioBufferCount();
}
int neededSpace = min(maxCount, nioBufferCount + count);
if (neededSpace > nioBuffers.length) {
//扩容操作,在缓存到本地缓存中,可以重复利用
nioBuffers = expandNioBufferArray(nioBuffers, neededSpace, nioBufferCount);
NIO_BUFFERS.set(threadLocalMap, nioBuffers);
}
if (count == 1) {
ByteBuffer nioBuf = entry.buf;
if (nioBuf == null) {
// 缓存ByteBuffer,因为如果它是派生的缓冲区,则可能需要创建一个新的ByteBuffer实例
// DirectByteBuffer#duplicate创建一个新的ByteBuffer
entry.buf = nioBuf = buf.internalNioBuffer(readerIndex, readableBytes);
}
nioBuffers[nioBufferCount++] = nioBuf;
} else {
ByteBuffer[] nioBufs = entry.bufs;
if (nioBufs == null) {
// cached ByteBuffers as they may be expensive to create in terms
// of Object allocation
entry.bufs = nioBufs = buf.nioBuffers();
}
for (int i = 0; i < nioBufs.length && nioBufferCount < maxCount; ++i) {
ByteBuffer nioBuf = nioBufs[i];
if (nioBuf == null) {
break;
} else if (!nioBuf.hasRemaining()) {
continue;
}
nioBuffers[nioBufferCount++] = nioBuf;
}
}
if (nioBufferCount == maxCount) {
break;
}
}
}
entry = entry.next;
}
this.nioBufferCount = nioBufferCount;
this.nioBufferSize = nioBufferSize;
return nioBuffers;
}
|
a.InternalThreadLocalMap 本地添加缓冲区
7.removeBytes 按字节删除Entry
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public void removeBytes(long writtenBytes) {
for (;;) {
Object msg = current();
if (!(msg instanceof ByteBuf)) {
assert writtenBytes == 0;
break;
}
final ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
final int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex();
final int readableBytes = buf.writerIndex() - readerIndex;
if (readableBytes <= writtenBytes) {
if (writtenBytes != 0) {
//ChannelProgressivePromise处理
progress(readableBytes);
writtenBytes -= readableBytes;
}
//删除Entry
//ChannelPromise成功处理,异步处理
remove();
} else { // readableBytes > writtenBytes
if (writtenBytes != 0) {
buf.readerIndex(readerIndex + (int) writtenBytes);
progress(writtenBytes);
}
break;
}
}
//nioBufferCount赋值为零,已经本地缓存初始化操作,赋值为空
clearNioBuffers();
}
|
a.writtenBytes写的字节小于Entry,Entry中还有数据要发送,主要ByteBuffer,在写时候把读位置也变动,这里不用去初始化操作;
十、RecvByteBufAllocator
分配一个新的接收缓冲区,其容量可能足够大以读取所有数据,而又足够小以不会浪费其空间。
NioSocketChannel读取默认使用AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
1.RecvByteBufAllocator接口类图
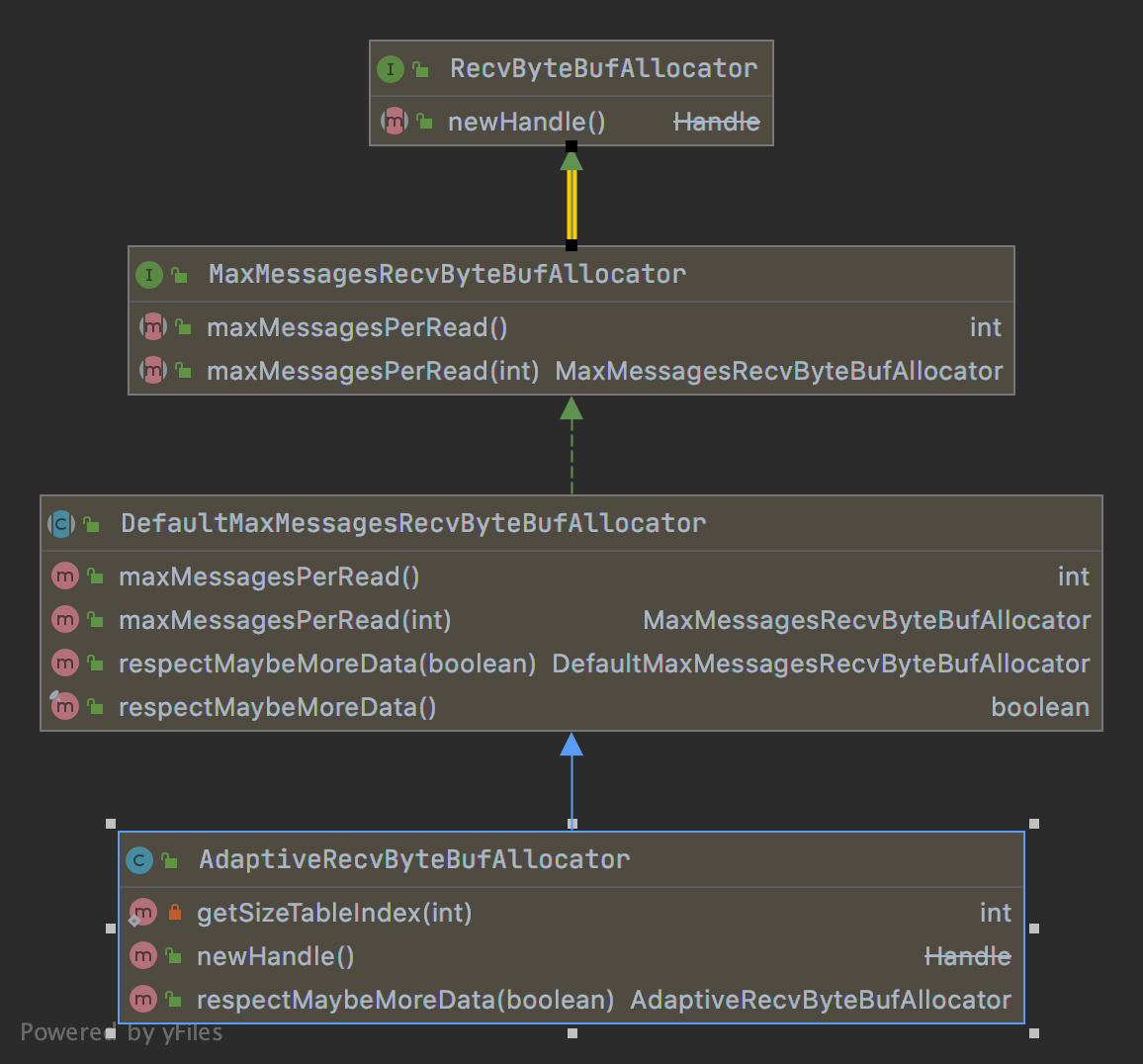
- guess 猜下次该用多大的接收缓冲区
- reset 重置一些统计参数
- 其他API名称顾名思义知道啥意思
2.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
根据反馈值自动增加和减少预测的缓冲区大小。
如果先前的读取完全填满了分配的缓冲区,它将逐渐增加预期的可读字节数。如果读取操作无法连续两次填充一定数量的已分配缓冲区,
则会逐渐减少预期的可读字节数。否则,它将继续返回相同的预测。
a.类图

b.newHandle 直接创建HandleImpl
3.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator#HandleImpl
a.类图结构
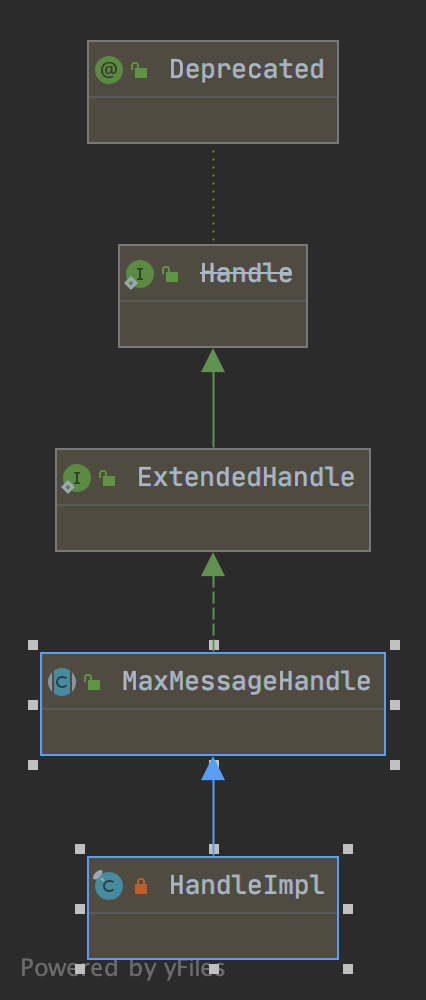
b.MaxMessageHandle
- 读取字节数统计
- 继续读的判断(continueReading)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public abstract class MaxMessageHandle implements ExtendedHandle {
private ChannelConfig config;
//读取消息的次数,默认1次
private int maxMessagePerRead;
private int totalMessages;
private int totalBytesRead;
private int attemptedBytesRead;//预计读取字节数
private int lastBytesRead;
//是否读取更多数据
private final boolean respectMaybeMoreData = DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator.this.respectMaybeMoreData;
private final UncheckedBooleanSupplier defaultMaybeMoreSupplier = new UncheckedBooleanSupplier() {
@Override
public boolean get() {
return attemptedBytesRead == lastBytesRead;
}
};
|
(1).reset重置统计的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Override
public void reset(ChannelConfig config) {
this.config = config;
maxMessagePerRead = maxMessagesPerRead();
totalMessages = totalBytesRead = 0;
}
|
(2).continueReading继续读
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Override
public boolean continueReading() {
return continueReading(defaultMaybeMoreSupplier);
}
@Override
public boolean continueReading(UncheckedBooleanSupplier maybeMoreDataSupplier) {
return config.isAutoRead() &&
(!respectMaybeMoreData || maybeMoreDataSupplier.get()) &&
totalMessages < maxMessagePerRead &&
totalBytesRead > 0;
}
|
- respectMaybeMoreData为false不用验证预计读取的字节大小
c.数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
//三个索引干嘛呢??
private final int minIndex;
private final int maxIndex;
private int index;
//获取读取容量大小
private int nextReceiveBufferSize;
//立即减少状态
private boolean decreaseNow;
|
d.AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator的类变量定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private static final int[] SIZE_TABLE;
static {
List<Integer> sizeTable = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 16; i < 512; i += 16) {
sizeTable.add(i);
}
for (int i = 512; i > 0; i <<= 1) {
sizeTable.add(i);
}
SIZE_TABLE = new int[sizeTable.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE_TABLE.length; i ++) {
SIZE_TABLE[i] = sizeTable.get(i);
}
}
|
SIZE_TABLE缓存大小,大小按区域,跟内存池划分有点相似;
- [16,512)按累加16
- [512,Int.Max)两倍增加
上面三个索引干嘛呢?就是保存缓存的下标,主要就是获取大小值;
(1).给大小值,是怎么获取大小呢?可能不在等于缓存值,是去最近小于还是最近大于;使用getSizeTableIndex方法
- 实现最常见二分查找
- size不在缓存中的值,取最近大于值的下标
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
private static int getSizeTableIndex(final int size) {
for (int low = 0, high = SIZE_TABLE.length - 1;;) {
if (high < low) {
return low;
}
if (high == low) {
return high;
}
int mid = low + high >>> 1;
int a = SIZE_TABLE[mid];
int b = SIZE_TABLE[mid + 1];
if (size > b) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (size < a) {
high = mid - 1;
} else if (size == a) {
return mid;
} else {
return mid + 1;
}
}
}
|
e.lastBytesRead记录读取的大小
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@Override
public void lastBytesRead(int bytes) {
// If we read as much as we asked for we should check if we need to ramp up the size of our next guess.
// This helps adjust more quickly when large amounts of data is pending and can avoid going back to
// the selector to check for more data. Going back to the selector can add significant latency for large
// data transfers.
// 如果预计读取的大小等于实际读取大小相同,则应检查是否需要增加下一个读取的大小。
// 当有大量数据待处理时,这有助于更快地进行调整,并且可以避免返回选择器以检查更多数据。
// 返回选择器可能会增加大量数据传输的延迟
if (bytes == attemptedBytesRead()) {
record(bytes);
}
super.lastBytesRead(bytes);
}
|
f.record 计算下一个读取的大小
- 实际读取大小[小于等于] SIZE_TABLE [index-2]
- nextReceiveBufferSize等于 SIZE_TABLE [index-1],最小值判断
- 实际读取大小[大于等于] nextReceiveBufferSize
- nextReceiveBufferSize 等于 SIZE_TABLE [index+4],最大值判断
- 减少读取大小,decreaseNow判断,进行二次操作;
- minIndex和maxIndex控制上下限制,默认1024和65536(64k)大小,调用getSizeTableIndex获取下标
- index默认值2,默认大小64;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private static final int INDEX_INCREMENT = 4;
private static final int INDEX_DECREMENT = 1;
private void record(int actualReadBytes) {
if (actualReadBytes <= SIZE_TABLE[max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)]) {
if (decreaseNow) {
index = max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
} else {
decreaseNow = true;
}
} else if (actualReadBytes >= nextReceiveBufferSize) {
index = min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
}
}
|
g.readComplete 调用record,计算下次读取的大小
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
public void readComplete() {
record(totalBytesRead());
}
|
h.allocate获取内存空间
MaxMessageHandle#allocate
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(guess());
}
|
HandleImpl#guess
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
public int guess() {
return nextReceiveBufferSize;
}
|
就是获取下次获取内存大小分配内存,最终逻辑交给record处理;在lastBytesRead方法和readComplete方法做调用record计算;






