【注意】最后更新于 March 12, 2019,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
一、简介
博客
Recyclers是本地线程堆栈的轻量级对象池,是抽象方法;Recycler主要提供了3个方法:
- get():获取一个对象。
- newObject(Handle):当没有可用对象时创建对象的实现方法。
- recycle(T, Handle):回收一个对象已经过期,用Handle#recycle
1.对象池数据结构图
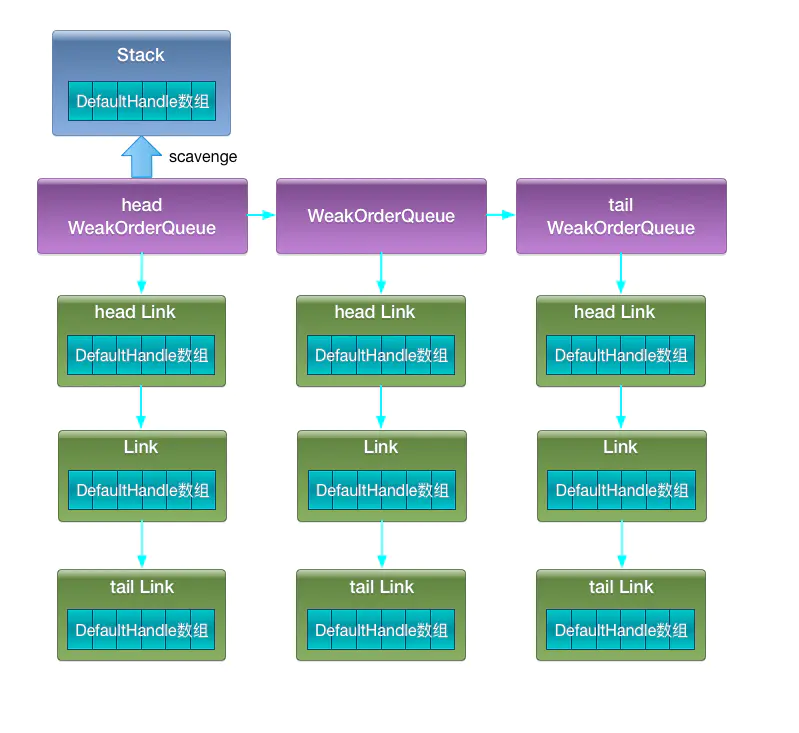
盗用上面博客图片
2.get获取对象流程
- 第一步先从本地线程中Stack获取对象,获取到立即返回,未获取到进行第二步;
- 第二步调用scavenge(),就是Stack的head已用其他线程WeakOrderQueue,进行回收对象到Stack中,立即返回;
3.recycle回收对象
- 第一步,调用DefaultHandle#recycle回收对象,判断Stack中的线程是否当前线程,是回收到Stack中;否进入第第二步;
- 第二步,回收到当前线程中Stack对应WeakOrderQueue;
a.为什么其他线程回收时,直接放到Stack中呢?
这一来Stack就会产生线程安全问题;回收对象时可能出现并发问题;
b.那么获取对象时产生并发问题,当前线程处理线程A的WeakOrderQueue回收Stack,线程A处理回收到WeakOrderQueue;
在WeakOrderQueue中保存链表+数据结构Link,定义head, tail属性,读去head操作,写就用tail;不存在数据竞争情况;
4.Recycler内部关系图
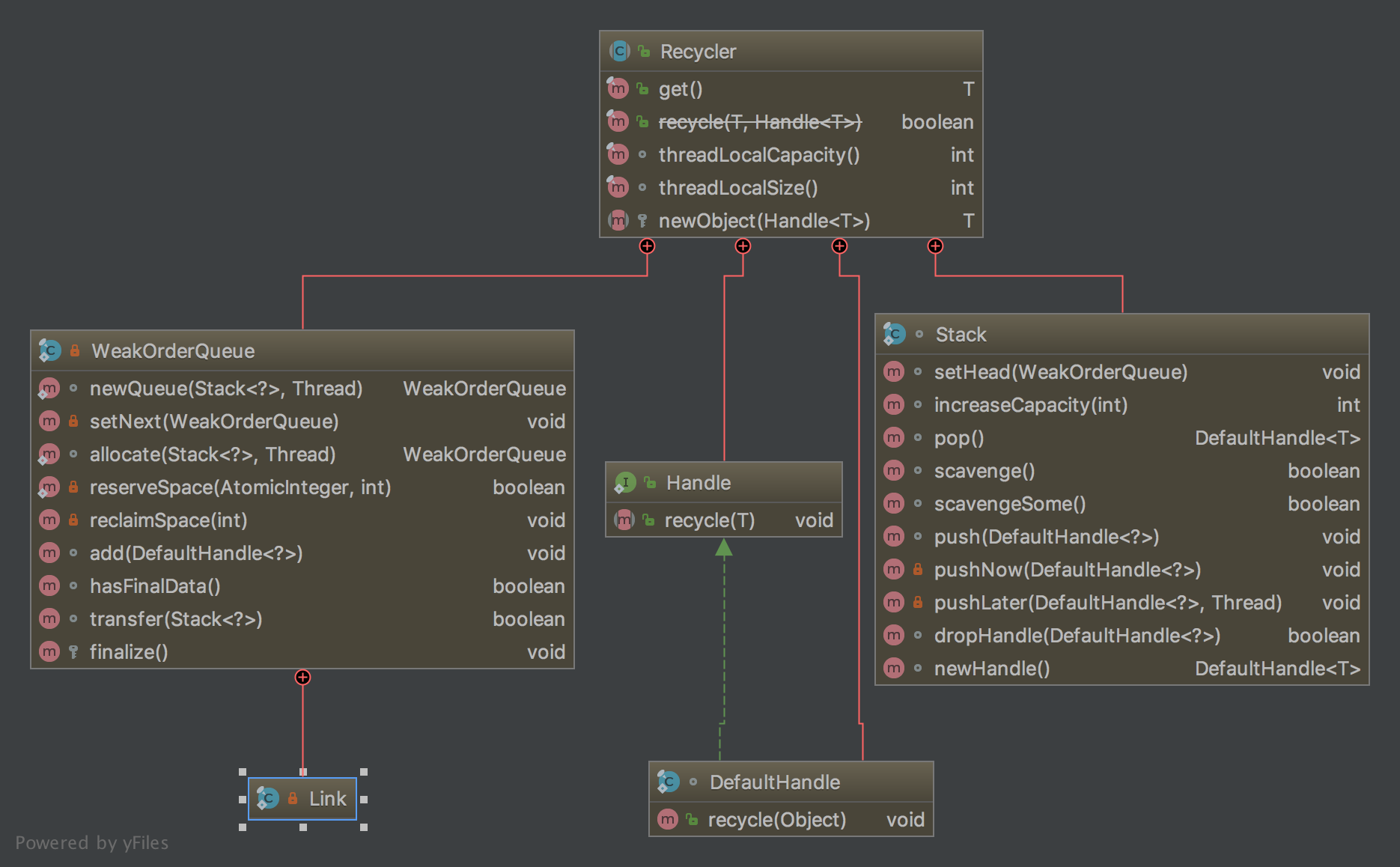
二、DefaultHandle
DefaultHandle就是就是Stack的包装对象,持有stack的引用,可以回收自己到stack中,以及回收对象;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
static final class DefaultHandle<T> implements Handle<T> {
private int lastRecycledId; //标记最新一次回收的线程id
private int recycleId; //也是一个标记,是用来回收前的校验的.
boolean hasBeenRecycled; //标记是否已经被回收
private Stack<?> stack; //持有stack的引用
private Object value;
DefaultHandle(Stack<?> stack) {
this.stack = stack;
}
@Override
public void recycle(Object object) {
if (object != value) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("object does not belong to handle");
}
stack.push(this); //可以回收自己到stack中
}
}
|
三、Stack
1.FastThreadLocal创建Stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private final FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>> threadLocal = new FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>>() { //FastThreadLocal是线程本地变量, 所以每个线程都对应一个自己的Stack.
@Override
protected Stack<T> initialValue() {
return new Stack<T>(Recycler.this, Thread.currentThread(), maxCapacityPerThread, maxSharedCapacityFactor,
ratioMask, maxDelayedQueuesPerThread);
}
};
|
2.数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
//用于回收
final Recycler<T> parent;
//持有线程
final Thread thread;
//容量,控制回收对象数量,其他线程可以回收对象,CAS控制并发;
//maxCapacity / maxSharedCapacityFactor方式控制大小
final AtomicInteger availableSharedCapacity;
//控制其他线程创建WeakOrderQueue数量
final int maxDelayedQueues;
//最大容量
private final int maxCapacity;
//DefaultHandle.hasBeenRecycled=fasle根据handleRecycleCount&ratioMask做判断条件进行回收
//默认8,每执行8次添加一个回收对象;具体逻辑在dropHandle方法中
private final int ratioMask;
private DefaultHandle<?>[] elements;
private int size;
private int handleRecycleCount = -1; // Start with -1 so the first one will be recycled.
//scavengeSome扫描其他线程WeakOrderQueue,变量保存
private WeakOrderQueue cursor, prev; // 指向当前的WeakOrderQueue 和 前一个
//WeakOrderQueue可能被GC线程回收,用volatile控制可见性
private volatile WeakOrderQueue head;
|
3.pop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
DefaultHandle<T> pop() {
int size = this.size;
if (size == 0) {
if (!scavenge()) {
return null;
}
size = this.size;
}
size --;
DefaultHandle ret = elements[size];
elements[size] = null;
if (ret.lastRecycledId != ret.recycleId) { //这两个应该相等
throw new IllegalStateException("recycled multiple times");
}
ret.recycleId = 0; //获取出的对象,置为0表示没有被回收
ret.lastRecycledId = 0; //获取出的对象,置为0表示没有被回收
this.size = size;
return ret;
}
|
a.scavenge 从其他线程的WeakOrderQueue中获取回收对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
boolean scavengeSome() { //尝试回收
WeakOrderQueue prev;
WeakOrderQueue cursor = this.cursor; //指向当前的指针
if (cursor == null) { //当前为null,就指向head,head也为null就跳出返回false
prev = null;
cursor = head;
if (cursor == null) {
return false;
}
} else {
prev = this.prev;
}
boolean success = false;
do {
//在WeakOrderQueue讲解
if (cursor.transfer(this)) {
success = true;
break;
}
WeakOrderQueue next = cursor.next;
if (cursor.owner.get() == null) { //线程被回收了
//cursor.owner.get() == null表示,GC已经回收该线程,也没必要同步数据
//是head,第一个WeakOrderQueue,这里不用处理,可能发送并发情况;
if (cursor.hasFinalData()) {
for (;;) {
if (cursor.transfer(this)) {
success = true;
} else {
break; //cursor.transfer(this)返回false,代表没有读取的数据了
}
}
}
if (prev != null) {
prev.setNext(next); //这是一个单向链表,只要改变prev的引用,老的节点会被回收的.
}
} else {
prev = cursor;
}
cursor = next;
} while (cursor != null && !success);
this.prev = prev;
this.cursor = cursor;
return success;
}
|
4.push
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
void push(DefaultHandle<?> item) { //会综合判断,如果是当前线程,直接放进数组中,如果不是,就先报错到WeakOrderQueue中.
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread == currentThread) {
// The current Thread is the thread that belongs to the Stack, we can try to push the object now.
pushNow(item);
} else {
// The current Thread is not the one that belongs to the Stack, we need to signal that the push //保存到WeakOrderQueue,等待回收.
// happens later.
pushLater(item, currentThread);
}
}
|
a.pushNow Stack持用当前线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
private void pushNow(DefaultHandle<?> item) {
if ((item.recycleId | item.lastRecycledId) != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already");
}
item.recycleId = item.lastRecycledId = OWN_THREAD_ID; //都更新为OWN_THREAD_ID,表示被回收过了
int size = this.size;
//达到容量值,不进行回收,dropHandle()方法验证是否能回收
if (size >= maxCapacity || dropHandle(item)) {
return;
}
if (size == elements.length) {
//扩容,按2倍扩容
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, min(size << 1, maxCapacity));
}
elements[size] = item;
this.size = size + 1;
}
|
b.dropHandle 验证是否能回收
DefaultHandle.hasBeenRecycled为false,根据ratioMask判断是否回收,能回收设置hasBeenRecycled为ture;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
boolean dropHandle(DefaultHandle<?> handle) {
if (!handle.hasBeenRecycled) {
if ((++handleRecycleCount & ratioMask) != 0) {
return true;
}
handle.hasBeenRecycled = true;
}
return false;
}
|
c.pushLater Stack不是当前线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private void pushLater(DefaultHandle<?> item, Thread thread) {
Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue> delayedRecycled = DELAYED_RECYCLED.get();
WeakOrderQueue queue = delayedRecycled.get(this);
if (queue == null) { //如果queue就需要创建一个
//大于上限,就放入一个DUMMY,表示满了
if (delayedRecycled.size() >= maxDelayedQueues) {
// Add a dummy queue so we know we should drop the object
delayedRecycled.put(this, WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY);
return;
}
// 检查是否已经达到延迟队列的最大数量,是否可以分配。
if ((queue = WeakOrderQueue.allocate(this, thread)) == null) {
return;
}
delayedRecycled.put(this, queue);
} else if (queue == WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY) {
return;
}
queue.add(item);
}
|
5.WeakOrderQueue的head控制,添加对象锁
1
2
3
4
|
synchronized void setHead(WeakOrderQueue queue) {
queue.setNext(head);
head = queue;
}
|
1.创建WeakOrderQueue
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
static WeakOrderQueue newQueue(Stack<?> stack, Thread thread) {
WeakOrderQueue queue = new WeakOrderQueue(stack, thread);
//stack.setHead(queue)必须在构造器外进行,防止对象溢出.
stack.setHead(queue); //这个stack,头指针指向 这个新创建的WeakOrderQueue
return queue;
}
|
四、WeakOrderQueue
1.FastThreadLocal缓存WeakOrderQueue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private static final FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>> DELAYED_RECYCLED = // 这也是一个线程本地变量,每个线程都有自己的Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>
new FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>>() { // 根据Stack可以获取到对应的WeakOrderQueue
@Override // 需要注意的是这边两个对象都有弱引用,WeakReference
protected Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue> initialValue() {
return new WeakHashMap<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>(); // 使用WeakHashMap,保证对key也就是Stack是弱引用; 一旦Stack没有强引用了, 会被回收的,WeakHashMap不会无限占用内存;
}
};
|
2.数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
//链表+数组
//数组数据控制同步Stack最大容量
private static final class Link extends AtomicInteger {
private final DefaultHandle<?>[] elements = new DefaultHandle[LINK_CAPACITY];
private int readIndex;
private Link next;
}
//数据链表
private Link head, tail;
// 执行下个线程中WeakOrderQueue
private WeakOrderQueue next;
//弱引用,
private final WeakReference<Thread> owner;
private final int id = ID_GENERATOR.getAndIncrement();
private final AtomicInteger availableSharedCapacity;
|
3.添加DefaultHandle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
void add(DefaultHandle<?> handle) {
handle.lastRecycledId = id; //更新最近一次回收的id, 注意这里只更新了lastRecycledId, recycleId没有更新, 等到真正回收的时候,会改成一致的.
Link tail = this.tail;
int writeIndex;
if ((writeIndex = tail.get()) == LINK_CAPACITY) {
//控制回收数量
if (!reserveSpace(availableSharedCapacity, LINK_CAPACITY)) { //判断剩余空间是否足够
// Drop it.
return;
}
// We allocate a Link so reserve the space
this.tail = tail = tail.next = new Link();
writeIndex = tail.get(); //tail这是一个自增的变量,每次tail.get()就表示放到末尾了
}
tail.elements[writeIndex] = handle; //把对应的handle引用放到末尾的数组里
handle.stack = null;
// 我们延迟设置以确保将handle.stack为空,然后再在拥有线程中将其取消为空。
// 这也意味着,如果我们看到索引已更新,我们将保证队列中某个元素的可见性
tail.lazySet(writeIndex + 1);
}
|
4.transfer 数据同步到Stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
boolean transfer(Stack<?> dst) {
Link head = this.head;
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
//清楚已读取数据
if (head.readIndex == LINK_CAPACITY) {
if (head.next == null) {
return false;
}
this.head = head = head.next;
}
final int srcStart = head.readIndex;
int srcEnd = head.get();
final int srcSize = srcEnd - srcStart;
if (srcSize == 0) {
return false;
}
final int dstSize = dst.size;
final int expectedCapacity = dstSize + srcSize;
if (expectedCapacity > dst.elements.length) {
final int actualCapacity = dst.increaseCapacity(expectedCapacity); //扩容
srcEnd = min(srcStart + actualCapacity - dstSize, srcEnd);
}
if (srcStart != srcEnd) {
final DefaultHandle[] srcElems = head.elements;
final DefaultHandle[] dstElems = dst.elements;
int newDstSize = dstSize;
for (int i = srcStart; i < srcEnd; i++) {
DefaultHandle element = srcElems[i];
if (element.recycleId == 0) {
element.recycleId = element.lastRecycledId; //前面的add方法只更新了lastRecycledId, transfer执行好了,需要更新recycleId一致,表示回收成功.
} else if (element.recycleId != element.lastRecycledId) { //recycleId=0才表示可回收的
throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already");
}
srcElems[i] = null; //成功了,就把WeakOrderQueue数组里置为空,释放对对象的引用
if (dst.dropHandle(element)) { //判断是否回收
// Drop the object.
continue;
}
element.stack = dst; //element是Link数组里的对象,stack指向目标stack
dstElems[newDstSize ++] = element; //目标Stack数组的尾部, 放入element
}
if (srcEnd == LINK_CAPACITY && head.next != null) { //如果head.next还有,就需要继续扩容
// Add capacity back as the Link is GCed.
reclaimSpace(LINK_CAPACITY); //扩容
this.head = head.next; //指向下一个,等待下一次循环继续上面的操作.transfer方法外层是被循环调用的.
}
head.readIndex = srcEnd; //下次从这里开始读
if (dst.size == newDstSize) { //如果相等则表示没有剩余空间了,返回false
return false;
}
dst.size = newDstSize; //目标数组size修改
return true;
} else {
// Stack数据已满不错处理
return false;
}
}
|
5.finalize gc回收调用方法
- WeakOrderQueue.next已被移除,可能会被GC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
try {
super.finalize();
} finally {
Link link = head;
while (link != null) {
//availableSharedCapacity.addAndGet(space)
reclaimSpace(LINK_CAPACITY);
link = link.next;
}
}
}
|
五、Recycler 源码分析
1.get
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public final T get() {
if (maxCapacityPerThread == 0) { // 通过修改maxCapacityPerThread=0可以关闭回收功能, 默认值是32768
return newObject((Handle<T>) NOOP_HANDLE);
}
Stack<T> stack = threadLocal.get(); // 获取当前线程对应的Stack
DefaultHandle<T> handle = stack.pop(); // 从对象池获取对象
if (handle == null) {
handle = stack.newHandle();
handle.value = newObject(handle); // 没有对象,则调用子类的newObject方法创建新的对象
}
return (T) handle.value;
}
|
2.配置信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
//最大容量 默认32768
private final int maxCapacityPerThread;
//其他线程容量控制因子
private final int maxSharedCapacityFactor;
//控制回收对象次数,默认每8次执行回收
private final int ratioMask;
//单线程控制创建WeakOrderQueue数量
private final int maxDelayedQueuesPerThread;
|


