【注意】最后更新于 June 1, 2017,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
ArrayBlockingQueue源码分析
简介
- ArrayBlockingQueue是一种基于数组实现的有界的阻塞队列。队列中的元素遵循先入先出(FIFO)的规则。
- ArrayBlockingQueue也支持公平和非公平策略。
一、BlockingQueue接口
java.util.concurrent包,实现BlockingQueue接口如图下:
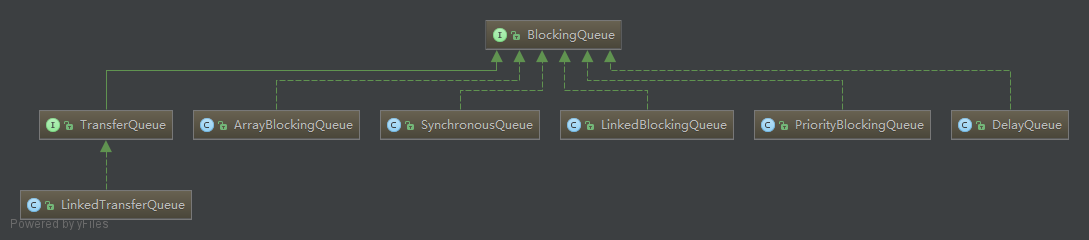
BlockingQueue接口实现
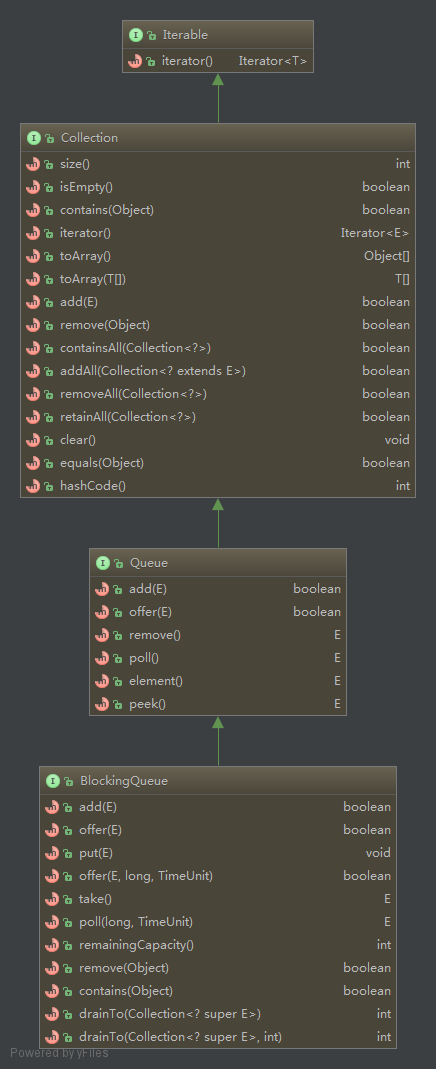
具体做BlockingQueue方法分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> {
/**
* 将指定的元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超过该队列的容量),
* 在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则抛出 IllegalStateException
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
* 将指定的元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超过该队列的容量),
* 在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则返回 false
*/
boolean offer(E e);
/**
* 将指定的元素插入此队列的尾部,如果该队列已满,则等待可用的空间
*/
void put(E e) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* 将指定的元素插入此队列的尾部,如果该队列已满,则在到达指定的等待时间之前等待可用的空间
*/
boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
/**
* 从队列头部获取并删除一个元素。
* 如果无法获取元素,当前操作线程等待,直到有元素可以被获取。
*/
E take() throws InterruptedException;
/**
* 从队列头部获取并删除一个元素。
* 如果无法获取元素,当前操作线程等待,直到有元素可以被获取或者给定时间超时。
* 如果超时,返回null。
*/
E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
/**
* 获取队列剩余容量。
*/
int remainingCapacity();
/**
* 移除队列中和给定元素相同的元素。
*/
boolean remove(Object o);
/**
* 判断队列中是否包含给定元素。
*/
public boolean contains(Object o);
/**
* 移除队列中所有的可用元素,并把它们添加到给定集合。
*/
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c);
/**
* 移除队列中不超过给定数量的可用元素,并把它们添加到给定集合。
*/
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements);
}
|
二、ArrayBlockingQueue内部实现
ArrayBlockingQueue实现AbstractQueue抽象类,继承BlockingQueue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/**
* Serialization ID. This class relies on default serialization
* even for the items array, which is default-serialized, even if
* it is empty. Otherwise it could not be declared final, which is
* necessary here.
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -817911632652898426L;
/** The queued items */
//内部元素的Object数组
final Object[] items;
/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
//入队元素使用的下标
int takeIndex;
/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
//出队元素使用的下标
int putIndex;
/** Number of elements in the queue */
//队列中的元素大小
int count;
/*
* Concurrency control uses the classic two-condition algorithm
* found in any textbook.
*/
/** Main lock guarding all access */
//显示重入锁,控制入队和出队元素
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
//队列为空等待条件
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
//队列满等待条件
private final Condition notFull;
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity and default access policy.
* 指定(固定)容量
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1}
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity and the specified access policy.
* 指定(固定)容量和指定的公平或者非公平策略
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked
* on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order;
* if {@code false} the access order is unspecified.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1}
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
/**
* Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)
* capacity, the specified access policy and initially containing the
* elements of the given collection,
* added in traversal order of the collection's iterator.
* 在集合的迭代器的遍历顺序中添加。
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked
* on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order;
* if {@code false} the access order is unspecified.
* @param c the collection of elements to initially contain
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is less than
* {@code c.size()}, or less than 1.
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
三、入队
1. offer方法
- offer(E e)
- offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 将指定元素插入该队列的尾部,如果队列已满,则等待空间的指定等待时间
```java
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is
* possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity,
* returning {@code true} upon success and {@code false} if this queue
* is full. This method is generally preferable to method {@link #add},
* which can fail to insert an element only by throwing an exception.
* 如果在队列尾部插入指定元素,如果不超过队列的容量,就可以立即执行,返回ture,如果此队列已满,false
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
insert(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
* 插入元素
*/
private void insert(E x) {
items[putIndex] = x;//保存数组元素
putIndex = inc(putIndex);//获取入队下标
++count;
notEmpty.signal(); //唤醒为空等待队列
}
/**
* Circularly increment i.
* 循环增量i
*/
final int inc(int i) {
return (++i == items.length) ? 0 : i;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting
* up to the specified wait time for space to become available if
* the queue is full.
* 将指定元素插入该队列的尾部,如果队列已满,则等待空间的指定等待时间
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos); //指定等待时间
}
insert(e);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
````
2. add方法
add(E e) 调用AbstractQueue抽象类中add方法,具体调用offer方法做判断,队列满了,throw IllegalStateException异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is
* possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity,
* returning {@code true} upon success and throwing an
* {@code IllegalStateException} if this queue is full.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws IllegalStateException if this queue is full
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return super.add(e);
}
|
AbstractQueue.add
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
|
3. put方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting
* for space to become available if the queue is full.
* 将指定元素插入该队列的尾部,如果队列已满,则等待。
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await(); //队列满等待条件
insert(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
四、出队
1. poll方法
- poll() 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null
- E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 获取并移除此队列的头部,队列为空时,在指定的等待时间前等待可用的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
// 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : extract();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private E extract() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
E x = this.<E>cast(items[takeIndex]); //获取元素
items[takeIndex] = null; //指定object下标元素赋值为null
takeIndex = inc(takeIndex); //出队下标
--count;
notFull.signal(); //唤醒等待队列满线程
return x;
}
//泛型转换
static <E> E cast(Object item) {
return (E) item;
}
//获取并移除此队列的头部,队列为空时,在指定的等待时间前等待可用的元素。
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos); //队列为空等待条件指定等待时间
}
return extract();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
2. take方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await(); //队列为空等待条件
return extract();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
3. peek方法
peek方法是java.util.Queue接口方法。获取队列的头部,不删除队列头部元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : itemAt(takeIndex);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
五、移除队列
1. remove方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
/**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,
* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such
* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such
* elements.
* Returns {@code true} if this queue contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a result of the call).
* 从该队列中删除指定元素的单个实例,如果它存在的话。更正式地,删除了一个元素
* <p>Removal of interior elements in circular array based queues
* is an intrinsically slow and disruptive operation, so should
* be undertaken only in exceptional circumstances, ideally
* only when the queue is known not to be accessible by other
* threads.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (int i = takeIndex, k = count; k > 0; i = inc(i), k--) {
if (o.equals(items[i])) {
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Deletes item at position i.
* Utility for remove and iterator.remove.
* Call only when holding lock.
*
*/
void removeAt(int i) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
// if removing front item, just advance
if (i == takeIndex) { // 删除队列头部
items[takeIndex] = null;
takeIndex = inc(takeIndex);
} else {
// slide over all others up through putIndex.
//删除不是队列头部,数据向左迁移,重新执行入队列小标
for (;;) {
int nexti = inc(i);
if (nexti != putIndex) {
items[i] = items[nexti];
i = nexti;
} else {
items[i] = null;
putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
}
--count;
notFull.signal();
}
|
2. clear方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
/**
* Atomically removes all of the elements from this queue.
* The queue will be empty after this call returns.
* 从原子上删除该队列中的所有元素。
*/
public void clear() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (int i = takeIndex, k = count; k > 0; i = inc(i), k--)
items[i] = null;
count = 0;
putIndex = 0;
takeIndex = 0;
notFull.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
3. drainTo方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
/** 移除队列中所有的可用元素,并把它们添加到给定集合。
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
checkNotNull(c);
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = takeIndex;
int n = 0;
int max = count;
while (n < max) {
c.add(this.<E>cast(items[i]));
items[i] = null;
i = inc(i);
++n;
}
if (n > 0) {
count = 0;
putIndex = 0;
takeIndex = 0;
notFull.signalAll();
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/** 移除队列中不超过给定数量的可用元素,并把它们添加到给定集合。
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
checkNotNull(c);
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = takeIndex;
int n = 0;
int max = (maxElements < count) ? maxElements : count;
while (n < max) {
c.add(this.<E>cast(items[i]));
items[i] = null;
i = inc(i);
++n;
}
if (n > 0) {
count -= n;
takeIndex = i;
notFull.signalAll();
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
五、Iterator 迭代器实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
/**
* Iterator for ArrayBlockingQueue. To maintain weak consistency
* with respect to puts and takes, we (1) read ahead one slot, so
* as to not report hasNext true but then not have an element to
* return -- however we later recheck this slot to use the most
* current value; (2) ensure that each array slot is traversed at
* most once (by tracking "remaining" elements); (3) skip over
* null slots, which can occur if takes race ahead of iterators.
* However, for circular array-based queues, we cannot rely on any
* well established definition of what it means to be weakly
* consistent with respect to interior removes since these may
* require slot overwrites in the process of sliding elements to
* cover gaps. So we settle for resiliency, operating on
* established apparent nexts, which may miss some elements that
* have moved between calls to next.
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
private int remaining; // Number of elements yet to be returned 队列元素数量
private int nextIndex; // Index of element to be returned by next (next下标)
private E nextItem; // Element to be returned by next call to next
private E lastItem; // Element returned by last call to next
private int lastRet; // Index of last element returned, or -1 if none 最后一个元素的索引返回,如果没有,则返回- 1
Itr() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
lastRet = -1;
if ((remaining = count) > 0)
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return remaining > 0;
}
public E next() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (remaining <= 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastRet = nextIndex;
E x = itemAt(nextIndex); // check for fresher value
if (x == null) {
x = nextItem; // we are forced to report old value
lastItem = null; // but ensure remove fails
}
else
lastItem = x;
while (--remaining > 0 && // skip over nulls
(nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = inc(nextIndex))) == null)
;
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void remove() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = lastRet;
if (i == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
lastRet = -1;
E x = lastItem;
lastItem = null;
// only remove if item still at index
if (x != null && x == items[i]) {
boolean removingHead = (i == takeIndex);
removeAt(i);
if (!removingHead)
nextIndex = dec(nextIndex);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* Circularly decrement i.
*/
final int dec(int i) {
return ((i == 0) ? items.length : i) - 1;
}
|
六、总结


