1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
|
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread())) //状态不是NEW,说明已有线程执行,CAS更新runner当前线程失败,说明其他线程比当前线程早一步。
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);//调用执行方法,调用throw异常,状态变成COMPLETING->EXCEPTIONAL
}
if (ran)
set(result); //成功执行,状态变成COMPLETING->NORMAL
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
//runner必须在设置了state之后再置空,避免run方法出现并发问题。
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
//这里还必须再读一次state,避免丢失中断。
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
/**
* Causes this future to report an {@link ExecutionException}
* with the given throwable as its cause, unless this future has
* already been set or has been cancelled.
*
* <p>This method is invoked internally by the {@link #run} method
* upon failure of the computation.
*
* @param t the cause of failure
*/
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/**
* Sets the result of this future to the given value unless
* this future has already been set or has been cancelled.
* 将这个未来的结果设置为给定值,除非这个未来已经被设置或被取消。
* <p>This method is invoked internally by the {@link #run} method
* upon successful completion of the computation.
*
* @param v the value
*/
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/**
* Removes and signals all waiting threads, invokes done(), and
* nulls out callable.
* 移除并发出所有等待的线程,调用done(),并取消callable。
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
/**
* Protected method invoked when this task transitions to state
* {@code isDone} (whether normally or via cancellation). The
* default implementation does nothing. Subclasses may override
* this method to invoke completion callbacks or perform
* bookkeeping. Note that you can query status inside the
* implementation of this method to determine whether this task
* has been cancelled.
* 当此任务转换为状态{@code isDone}时调用受保护的方法(通常或通过取消)。
* 默认实现什么都不做。子类可以重写此方法来调用完成回调或执行簿记。
* 请注意,您可以查询此方法执行内的状态,以确定此任务是否已被取消。
*/
protected void done() { }
/**
* Ensures that any interrupt from a possible cancel(true) is only
* delivered to a task while in run or runAndReset.
*/
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
// It is possible for our interrupter to stall before getting a
// chance to interrupt us. Let's spin-wait patiently.
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield(); // wait out pending interrupt
// assert state == INTERRUPTED;
// We want to clear any interrupt we may have received from
// cancel(true). However, it is permissible to use interrupts
// as an independent mechanism for a task to communicate with
// its caller, and there is no way to clear only the
// cancellation interrupt.
//
// Thread.interrupted();
}
/**
* Executes the computation without setting its result, and then
* resets this future to initial state, failing to do so if the
* computation encounters an exception or is cancelled. This is
* designed for use with tasks that intrinsically execute more
* than once.
* 执行计算而不设置其结果,然后将此未来重置为初始状态,如果计算遇到异常或被取消,
* 则不执行此操作。这是设计用于与本质上执行多次的任务。
* @return true if successfully run and reset
*/
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
boolean ran = false;
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
c.call(); // don't set result
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
setException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
return ran && s == NEW;
}
|
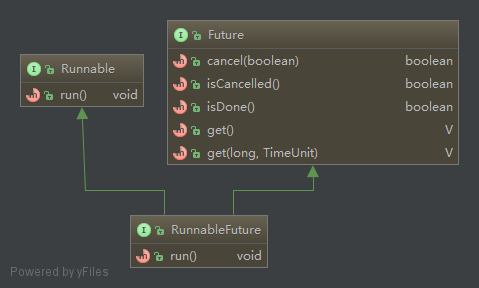 RunnableFuture继承Runnable接口和Future
RunnableFuture继承Runnable接口和Future RunnableFuture继承Runnable接口和Future
RunnableFuture继承Runnable接口和Future