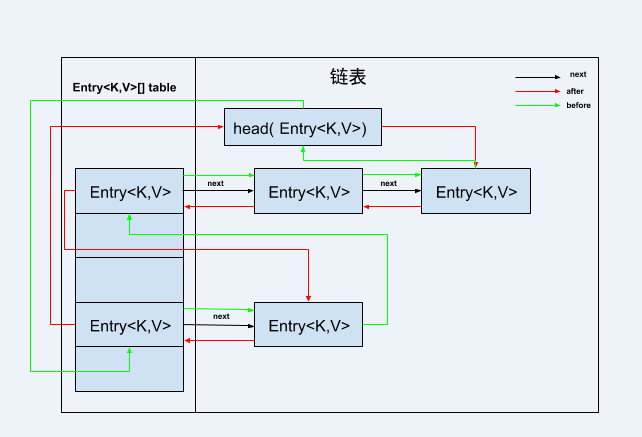
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
|
/**
* Called by superclass constructors and pseudoconstructors (clone,
* readObject) before any entries are inserted into the map. Initializes
* the chain.
*重写父类的init()方法(HashMap中的init方法为空),
*该方法在父类的构造方法和Clone、readObject中在插入元素前被调用,
*初始化一个空的双向循环链表,头结点中不保存数据,头结点的下一个节点才开始保存数据。
*/
@Override
void init() {
header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null);
header.before = header.after = header;
}
/**
* Transfers all entries to new table array. This method is called
* by superclass resize. It is overridden for performance, as it is
* faster to iterate using our linked list.
*覆写HashMap中的transfer方法,它在父类的resize方法中被调用, 扩容后,将key-value对重新映射到新的newTable中
*重写该方法的目的是为了提高复制的效率, 这里充分利用双向循环链表的特点进行迭代,不用对底层的数组进行for循环。
*/
@Override
void transfer(HashMap.Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after) {
if (rehash)
e.hash = (e.key == null) ? 0 : hash(e.key);
int index = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[index];
newTable[index] = e;
}
}}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
*重写写该方法的目的同样是为了提高查询的效率, 利用双向循环链表的特点进行查询,少了对数组的外层for循环
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
// Overridden to take advantage of faster iterator
if (value==null) {
for (Entry e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after)
if (e.value==null)
return true;
} else {
for (Entry e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after)
if (value.equals(e.value))
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* 注意这里的recordAccess方法,
*如果链表中元素的排序规则是按照插入的先后顺序排序的话,该方法什么也不做,
*如果链表中元素的排序规则是按照访问的先后顺序排序的话,则将e移到链表的末尾处。
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}
/**
* Removes all of the mappings from this map.
* The map will be empty after this call returns.
* 清空HashMap,并将双向链表还原为只有头结点的空链表
*/
public void clear() {
super.clear();
header.before = header.after = header;
}
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
/**删除最老条目判断*/
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
}
}
/**
* This override differs from addEntry in that it doesn't resize the
* table or remove the eldest entry.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
/**每次插入Entry时,都将其移到双向链表的尾部*/
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map should remove its eldest entry.
* This method is invoked by <tt>put</tt> and <tt>putAll</tt> after
* inserting a new entry into the map. It provides the implementor
* with the opportunity to remove the eldest entry each time a new one
* is added. This is useful if the map represents a cache: it allows
* the map to reduce memory consumption by deleting stale entries.
* 如果此Map应删除其最老的条目,则返回<tt> true </ tt>。 在将新条目插入到Map中之后,
* 该方法由<tt> put </ tt>和<tt> putAll </ tt>调用。
* 它为实施者提供每次添加新的条目时删除最老条目的机会。
* 如果地图代表一个缓存,这是非常有用的:它允许地图通过删除陈旧的条目来减少内存消耗。
* <p>Sample use: this override will allow the map to grow up to 100
* entries and then delete the eldest entry each time a new entry is
* added, maintaining a steady state of 100 entries.
* <pre>
* private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 100;
*
* protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
* return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
* }
* </pre>
*
* <p>This method typically does not modify the map in any way,
* instead allowing the map to modify itself as directed by its
* return value. It <i>is</i> permitted for this method to modify
* the map directly, but if it does so, it <i>must</i> return
* <tt>false</tt> (indicating that the map should not attempt any
* further modification). The effects of returning <tt>true</tt>
* after modifying the map from within this method are unspecified.
*
* <p>This implementation merely returns <tt>false</tt> (so that this
* map acts like a normal map - the eldest element is never removed).
*
* @param eldest The least recently inserted entry in the map, or if
* this is an access-ordered map, the least recently accessed
* entry. This is the entry that will be removed it this
* method returns <tt>true</tt>. If the map was empty prior
* to the <tt>put</tt> or <tt>putAll</tt> invocation resulting
* in this invocation, this will be the entry that was just
* inserted; in other words, if the map contains a single
* entry, the eldest entry is also the newest.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the eldest entry should be removed
* from the map; <tt>false</tt> if it should be retained.
*/
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
|