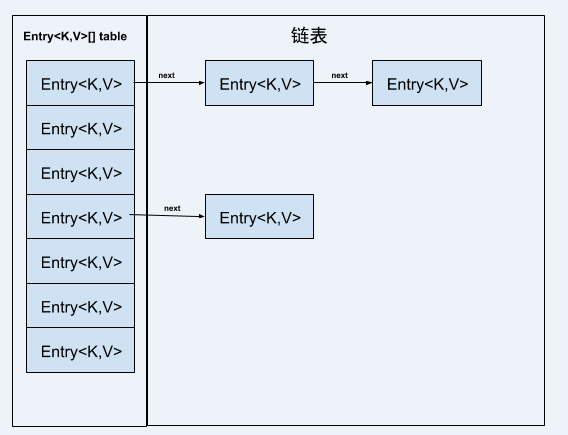
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
|
/**
* Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
* result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
* critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
* 检索对象哈希码,并将补充哈希函数应用于结果哈希,从而抵御不良品质的哈希函数。 这是至关重要的,
* 因为HashMap使用二分之二长度的哈希表,否则会遇到低位不相同的hashCodes的冲突。 注意:空键总是映射到哈希值0,因此索引为0。
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
/**如果key是字符串,调用un.misc.Hashing.stringHash32生成hash值*/
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
/**此函数确保每个位位置上仅有常数倍数不同的hashCode具有有界数量的冲突(默认负载系数约为8)。*/
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
* 返回hash值的索引,采用除模取余法,h & (length-1)操作 等价于 hash % length操作, 但&操作性能更优
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*Map存入一个简直对。如果Key存在,则替换
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
/**如果table == EMPTY_TABLE,那么这时创建表的初始容量。*/
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
/**对key为null的键值对调用putForNullKey处理*/
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
/**生成key hash值*/
int hash = hash(key);
/**获取数组hash值的索引*/
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
/**查找Key是否相等,则替换*/
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
* 将指定的键,值和哈希码的新条目添加到指定的存储桶。 如果适当,扩容。
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//扩容 按2倍扩展
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
* 插入单链表表头
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
/**
* Offloaded version of put for null keys
* 操作key为null键
*/
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
//查找key为null键,则替换
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
/**
* This method is used instead of put by constructors and
* pseudoconstructors (clone, readObject). It does not resize the table,
* check for comodification, etc. It calls createEntry rather than
* addEntry.
* 使用这种方法代替构造函数和伪构造函数(clone,readObject)。 它不调整表的大小,检查comodification等。它调用createEntry而不是addEntry。
*/
private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
int hash = null == key ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
/**
* Look for preexisting entry for key. This will never happen for
* clone or deserialize. It will only happen for construction if the
* input Map is a sorted map whose ordering is inconsistent w/ equals.
* 查找Key是否相等,则替换
*/
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
}
/**
* 指定Map集合添加到HashMap中
*/
private void putAllForCreate(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
putForCreate(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
/**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for
* any of the keys currently in the specified map.
* 将指定Map集合复制目前Map。如果有存在相同key值,则替换。
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return;
/**如果table == EMPTY_TABLE,那么这时创建表的初始容量。*/
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable((int) Math.max(numKeysToBeAdded * loadFactor, threshold));
}
/*
* Expand the map if the map if the number of mappings to be added
* is greater than or equal to threshold. This is conservative; the
* obvious condition is (m.size() + size) >= threshold, but this
* condition could result in a map with twice the appropriate capacity,
* if the keys to be added overlap with the keys already in this map.
* By using the conservative calculation, we subject ourself
* to at most one extra resize.
* 如果要添加的映射数大于或等于阈值,则展开映射。 这是保守的 明显的条件是(m.size()+ size)> = threshold,
* 但是如果要添加的键与已经在该映射中的键重叠,则此条件可能导致具有两倍相应容量的映射。 通过使用保守的计算,我们最多只能调整一次调整大小。
*/
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
}
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
|